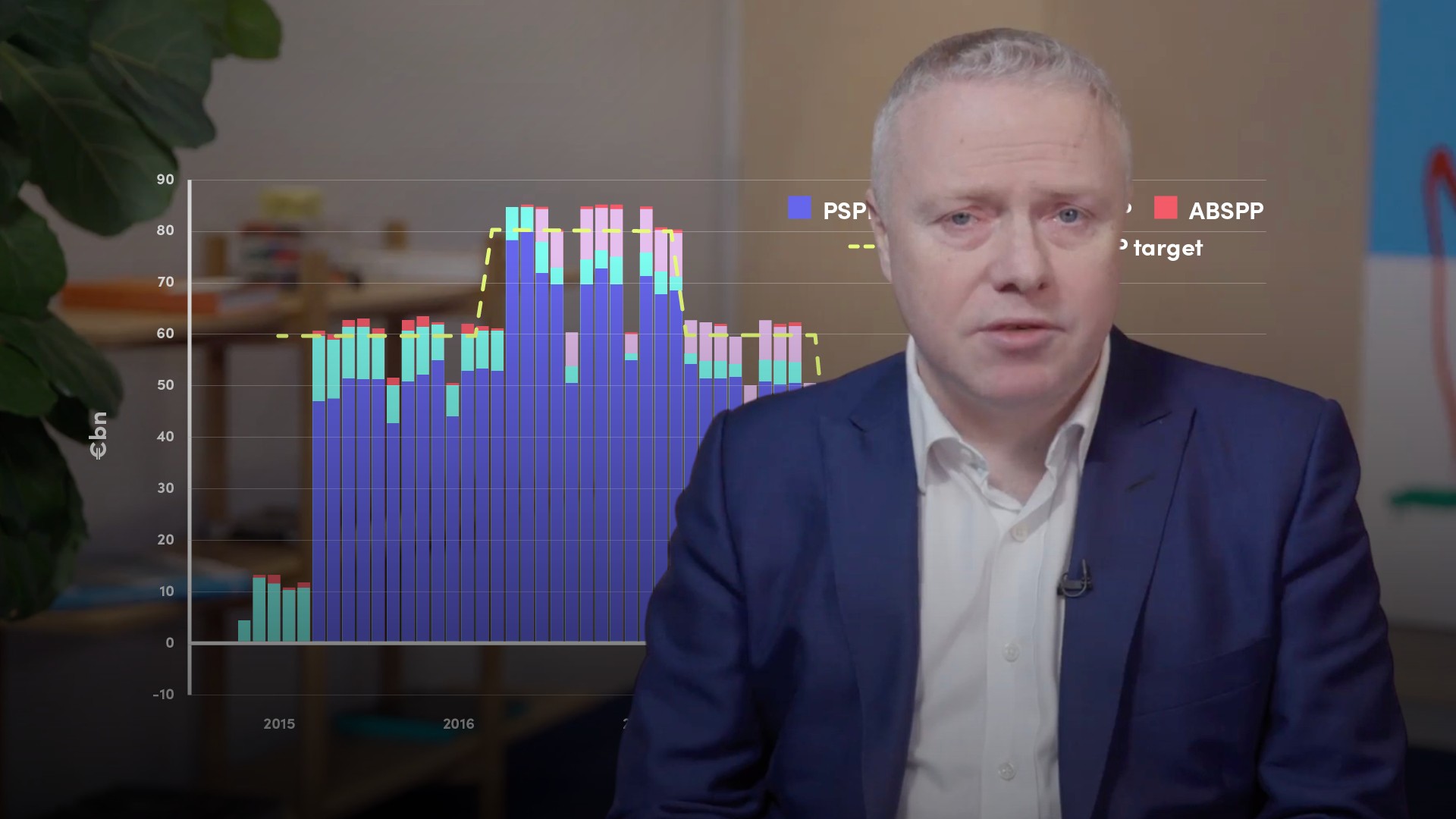
European Economic and Monetary Union (EMU)
The European Union’s Economic and Monetary Union (EMU) is a major policy initiative designed to integrate the bloc’s economies (27 countries as of March 2021). The plan was originally launched in 1992, just before the Maastricht Treaty that created the EU was signed. At its heart, EMU is a political and economic initiative to closely co-ordinate each country’s economic and fiscal policies through common policies and, for 19 of the EU’s 27 member States (as of March 2021), the euro common currency. EMU is the culmination of efforts that started in 1957 when the Treaty of Rome was signed. The thinking behind EMU is that economic integration allows the benefits of scale and efficiency to be realised under a framework that creates economic stability and allows for higher growth and more employment.