A Closer Look at Scope 3 Emissions

Sam Hope
5 years: Carbon Markets
Scope 3 emissions are the largest and hardest to calculate. Join Sam Hope as he breaks down each of the 15 categories of scope 3 emissions.
Scope 3 emissions are the largest and hardest to calculate. Join Sam Hope as he breaks down each of the 15 categories of scope 3 emissions.

A Closer Look at Scope 3 Emissions
11 mins 44 secs
Key learning objectives:
Define scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions
Understand the benefits of calculating scope 3 emissions
Outline the categories of scope 3 emissions
Overview:
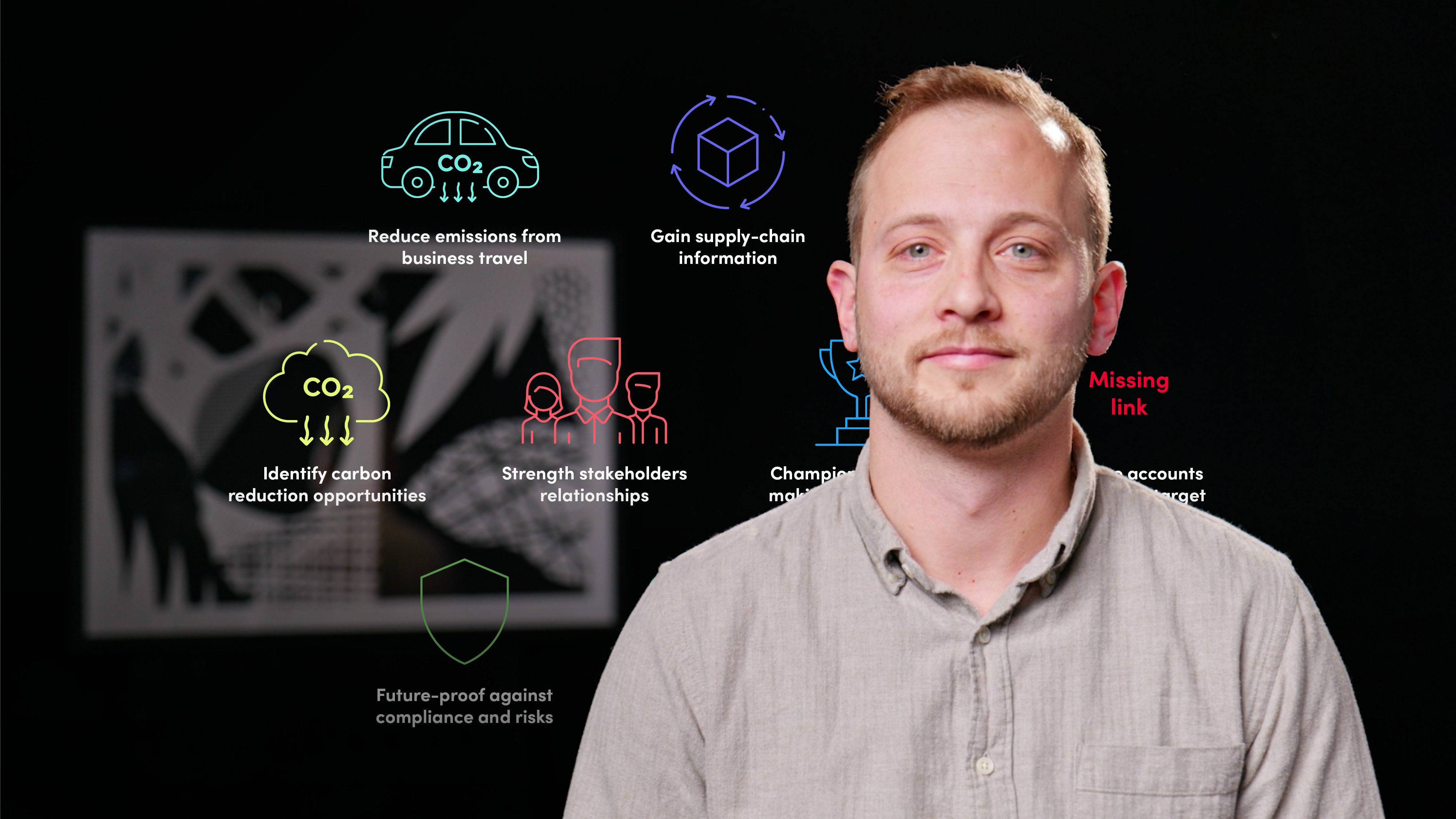
Scope 3 covers all other indirect emissions that occur in a company’s value chain. As a result, this is a complex and difficult area of footprint to assess. Companies with large value chains can find benefits to calculating these emissions, including identifying carbon reduction and energy efficiency opportunities, future-proofing against compliance and energy resource risks and preparing your accounts for your net zero target. There are 15 scope 3 categories in total which can be split into upstream, operations and downstream emissions.
What are scope 1 emissions?
Scope 1 covers direct emissions from owned or controlled sources, such as diesel used in fleet vehicles or natural gas used to heat company buildings.
What are scope 2 emissions?
Scope 2 covers indirect emissions from the use of purchased energy. In most cases this is limited to purchased electricity.
What are scope 3 emissions?
Scope 3 covers all other indirect emissions that occur in a company’s value chain. As a result, this is a complex and difficult area of footprint to assess.
What are the benefits of calculating scope 3 emissions?
1. Engaging with employees to reduce emissions from business travel and employee commuting
2. Gaining valuable supply-chain information
3. Assessing where emissions hotspots exist
4. Identifying carbon reduction and energy efficiency opportunities
5. Strengthening relationships with stakeholders
6. Engaging and championing those businesses in your value chain that are making better choices
7. Preparing your accounts for your net zero target
8. Future-proofing against compliance and energy resource risks
9. Protecting your business from reputational risk
10. Getting started with supply chain carbon insetting projects
What are the 15 categories of scope 3 emissions?
Upstream scope 3 emissions
Category 1 - Purchased goods and services
All upstream extraction, production and transportation emissions of goods and services purchased by the reporting organisation.
Category 2 - Capital goods
All upstream extraction, production and transportation emissions related to the purchase of capital goods, such as plant machinery and fleet vehicles.
Category 3 - Fuel and energy related activities
All upstream extraction, production and transportation emissions related to the fuel and energy purchased by the reporting organisation. Basically the process emissions of the raw materials, excluding combustion.
Category 4 - Upstream transportation and distribution
Transportation and distribution of products purchased by the reporting company, between a company’s tier 1 suppliers and its own operations.
Category 8 - Upstream leased assets
Operation of assets leased by the reporting company in the reporting year that are not included in scope 1 and scope 2.
Scope 3 emissions from operations
Category 5 - Waste generated in operations
The scope 1 and scope 2 emissions of waste management suppliers that occur during waste disposal or treatment and optional emissions from transportation of waste.
Category 6 - Business travel
The scope 1 and scope 2 emissions of transportation carriers that occur during use of vehicles for business travel.
Category 7 - Employee commuting
Transportation of employees between their homes and their worksites during the reporting year in vehicles not owned by the reporting company. This includes the scope 1 and scope 2 emissions of employees and transportation providers that occur during use of vehicles.
Downstream scope 3 emissions
Category 9 - Downstream transportation
Transportation and distribution of products sold by the reporting company to the end consumer and in vehicles and facilities not owned or controlled by the reporting company.
Category 10 - Processing of sold products
The scope 1 and scope 2 emissions of downstream companies that occur during processing of company-owned products.
Category 11 - Use of sold products
The direct use-phase emissions of sold products over their expected lifetime.
Category 12 - End-of-life treatment of sold products
Waste disposal and treatment related emissions of products sold by the reporting company at the end of their useful life.
Category 13 - Downstream leased assets
Operation of assets owned by the reporting company and leased to other entities in the reporting year, not already included in scope 1 and scope 2.
Category 14 - Franchises
The scope 1 and scope 2 emissions of franchisees that occur during operation of franchises from energy use and reported by the franchisor.
Category 15 - Investments
Operation of investments, including equity and debt investments and project finance in the reporting year that are not included in scope 1 or scope 2 emissions.

Sam Hope
There are no available Videos from "Sam Hope"

