Benefits of Blockchain

Brian Marcel
35 years: Financial technology
Blockchain is an amazing new technology that is going to change the world just like barcodes did back in the 70s. In this first video of the series, Brian will explain the history of barcodes in trade and discuss how blockchains will enhance these existing barcode systems.
Blockchain is an amazing new technology that is going to change the world just like barcodes did back in the 70s. In this first video of the series, Brian will explain the history of barcodes in trade and discuss how blockchains will enhance these existing barcode systems.

Benefits of Blockchain
8 mins 59 secs
Key learning objectives:
Identify the uses and benefits of the existing barcode system
Explain the uses and benefits of the blockchain technology
Define ‘smart contracts’
Overview:
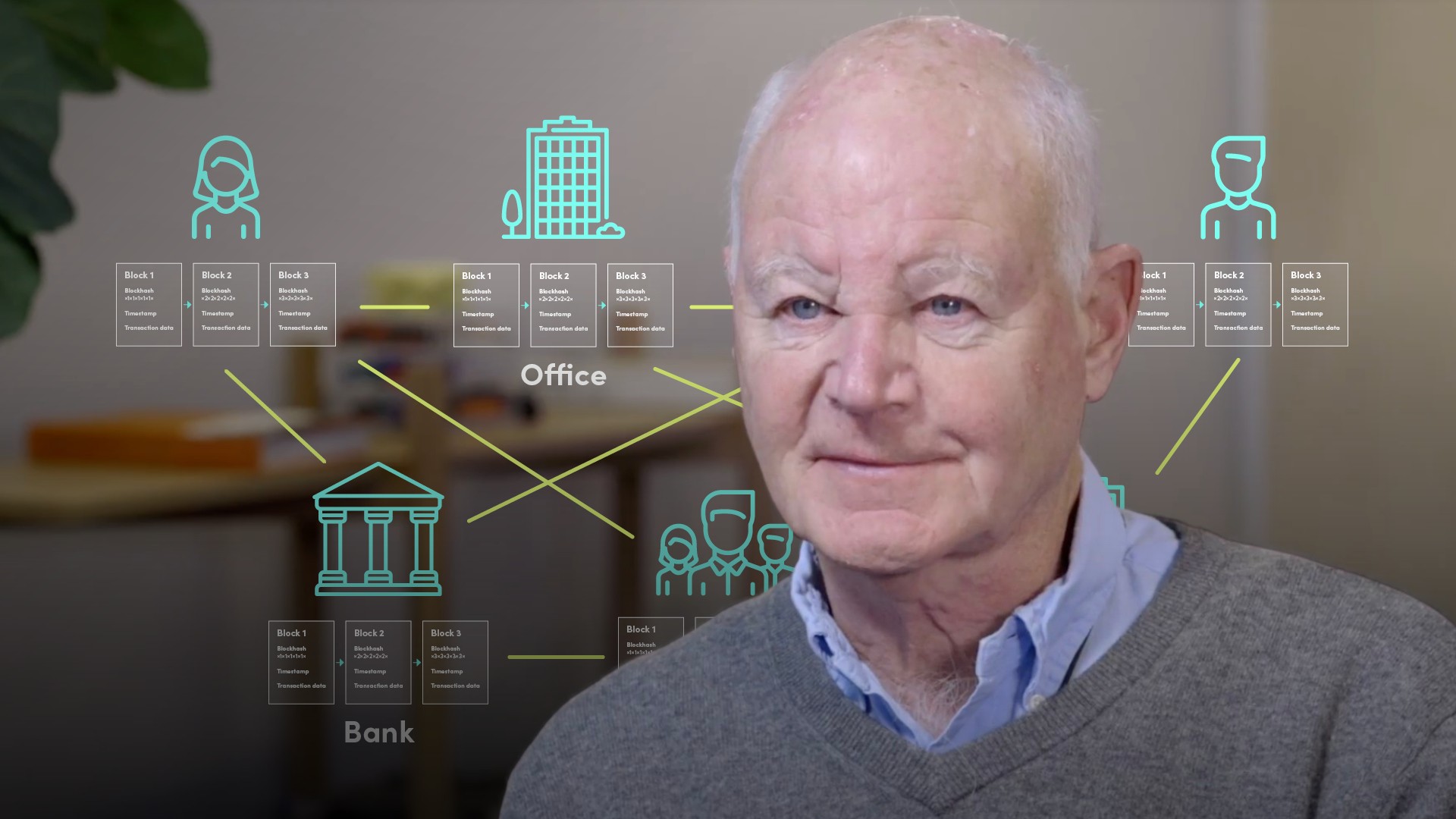
Blockchain is the underlying technology behind Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.. The most prevalent applications of blockchains are in financial services such as payment schemes. But what will bring the most development, is when corporates realise the benefits of using this technology.
What did the intervention of the barcode do for trade?
Barcodes eliminate human intervention, and thus errors, as well as speeding up the data entry process. A simple scan of a barcode enters data which can be manipulated at will.Uses of the barcode system:
- Inventory Management
- Inventory Management is the most prevalent solution using barcodes, and ensures all businesses can enjoy efficiencies and stock accuracy previously only dreamt of. For example, retailers like Tesco are able to track their stock from the moment it enters their system, to the point of sale, enabling immediate stock replenishment.
- Healthcare
- Blood bags are labelled with blood type barcodes and tracked through the system and patients are given barcoded wristbands, so they are given the correct blood and/or medicine thus dramatically reducing deaths from incorrect administration.
- Global Trade
- Barcodes are used to ensure there is a numbering system for containers and shipping units, enabling companies to track where their shipments are at any one time. This also reduces time and adds efficiency to the supply chain.
What can go wrong if barcode systems are not used?
If you compare trade in China with other countries, it can be seen how important barcodes are. For example, supply chains in China are fragmented due to the lack of a national carrier. So, shipments have to be shipped from company to company for long distances, thus giving rise to damaged goods from excessive handling and inefficiencies in traceability as some companies are still using pen and paper, some spreadsheets and some without computer systems.In what ways will blockchain enhance existing barcode systems?
- Products and services can be tracked and traced faster and with confidence; it is in the supply chain that early adoption is seen due to the ease of storing data that has been validated and is available for viewing anytime and anywhere by accessing the portal.
- Authentication and provenance of medicines, food and art can be trusted, thus the threat of forgery will be eliminated.
- Governments can have their voters details stored on the blockchain to prevent double voting, putting trust into the financial system
What are the benefits of blockchain?
- It is a decentralised ledger
- A decentralised ledger is distributed amongst the computer nodes who run the blockchain, so there is no single point of failure, and more importantly, no single person or organisation controlling the network. To be part of the blockchain ecosystem, each person adding a transaction has to be validated for, and thus, everyone can trust the people and the transactions that make up the blockchain community
- It carries a cryptographic fingerprint
- A cryptographic fingerprint, unique to each block, is a proof of work by miners who have to solve a complicated algorithm using a great deal of computing power to add a block to the blockchain. Each block of transactions is hashed and copied to each node, a new block will include a hash of the whole history, practically making any changes of the historical data extremely time consuming and costly.
- Represents a single version of the truth
- If you have a supply chain where the actors or data isn’t trusted as authentic, the blockchain provides an opportunity to filter such actors and enables trading only with authentic people
- Transparency
- Everyone who has been approved in the ecosystem has visibility of the data, anytime they want, through logging into the portal. Depending on the business model, you can design it so that only some actors are allowed to view data, or that everyone is allowed to view it.
What is a ‘smart contract’?
A useful side benefit of the blockchain is a piece of software that creates ‘smart contracts’. These sit behind the blockchain and automatically execute certain events, i.e. a payment for a shipment. This is similarly achieved without any intervention from banks or any third parties.
Brian Marcel
There are no available Videos from "Brian Marcel"

