Board Audit Committees II

Bill Gallagher
30 years: Credit & banking
In this video, Bill Gallagher continues to delve into board audit committees and explains the role of audit committees with regards to dealing with external auditors and the increasing importance of ESG oversight.
In this video, Bill Gallagher continues to delve into board audit committees and explains the role of audit committees with regards to dealing with external auditors and the increasing importance of ESG oversight.

Board Audit Committees II
7 mins 38 secs
Key learning objectives:
Understand the role of the audit committee in ensuring the independence of external auditors
Understand the audit committees' growing role in ESG oversight
Outline the failures at Enron that ultimately led to its demise
Overview:
An audit committee plays a vital role in a company's corporate governance, ensuring the accuracy of financial reports and overseeing external auditors. It monitors their independence, creates and monitors non-audit engagement policies, reviews auditors’ work, and advises on appointments or removals. Recently, environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues have gained prominence. Hence, audit committees now also oversee ESG risks and compliance with reporting initiatives. They assess ESG policies and programs, monitor performance, and evaluate ESG-related risks and their alignment with strategic priorities. A prominent failure of independent governance can be shown through Enron's collapse, which underlined the need for independent audit committees, as failure can lead to substantial losses.
What role does the audit committee play in ensuring independent judgement of external auditors?
The audit committee assures stakeholders of financial statement integrity by overseeing external auditors, appointed by shareholders. Maintaining auditor independence requires careful balancing as close relationships with management can risk perceived or actual conflicts of interest. Similarly, disproportionate non-audit income can compromise perceived independence.
Thus, the audit committee's key functions involve monitoring auditor independence, managing non-audit engagements, reviewing auditor work, and advising on their appointment, retention, or removal.
How is the audit committee's role expanding to include ESG oversight?
In recent years, the committee's role has expanded to include oversight of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues.
The committee ensures compliance with reporting standards such as SASB, GRI, and TCFD, overseeing adherence to guidelines, approving ESG disclosures, and working with auditors to assess ESG risks and opportunities.
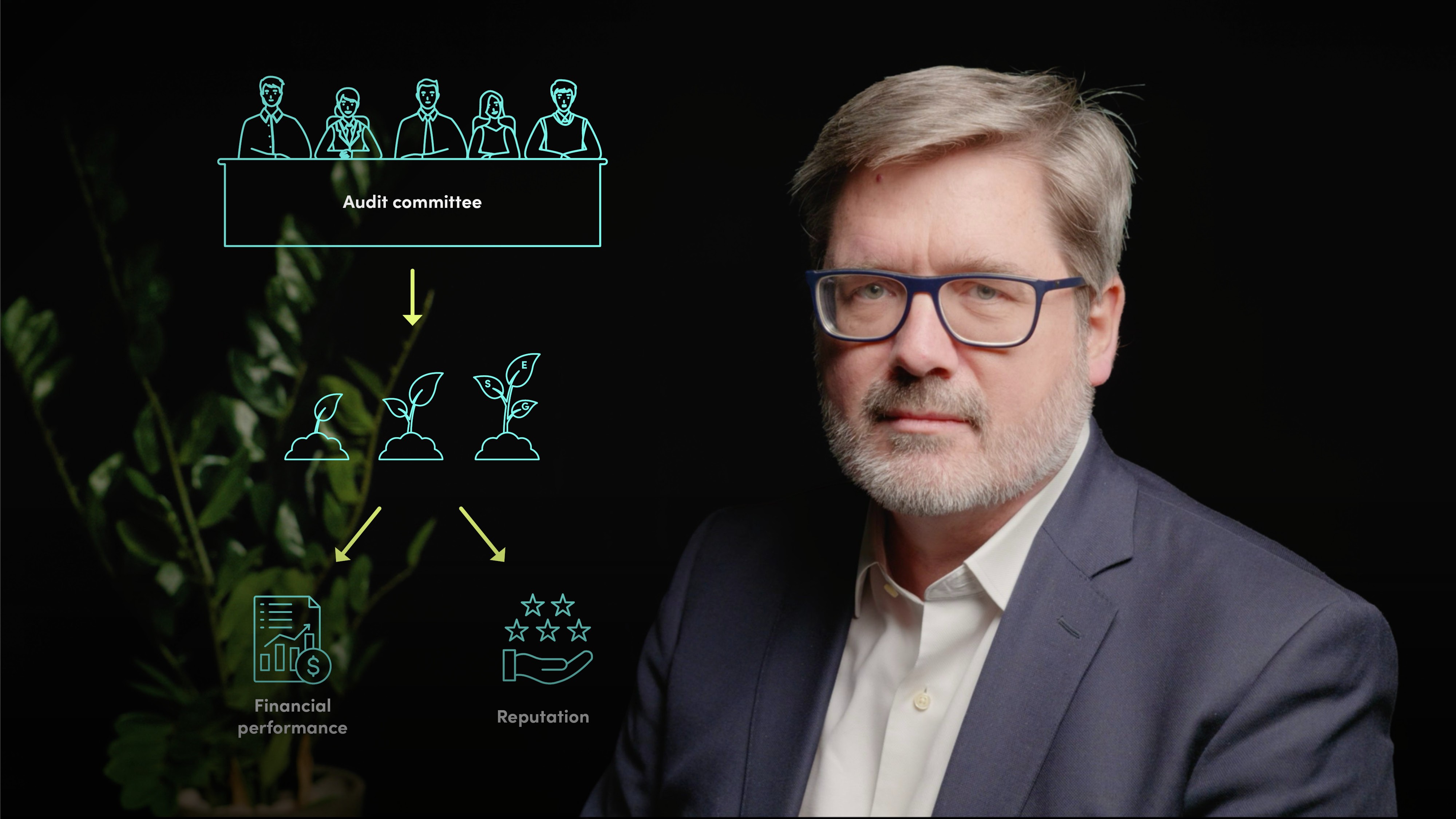
The committee's responsibilities regarding ESG include reviewing policies and programs, assessing the company's ESG reporting adequacy, and providing input on environmental management systems, social and human rights policies, and governance frameworks.
Additionally, the committee monitors the company's ESG performance, providing oversight of the controls and processes supporting ESG reporting, and reporting regularly to the board of directors, investors, and other stakeholders on ESG performance.
Lastly, the committee assesses ESG risks, considering their potential impact on financial performance and reputation, and their alignment with the company's strategic priorities.
What failures at Enron led to its demise?
Enron's demise resulted from fraudulent accounting that inflated profits and hid debt, overlooked by an audit committee that lacked true independence from management. Their failure to address accounting irregularities and employee concerns led to the company's collapse, massive investor losses, and a significant impact on the US economy. This debacle also caused the dissolution of Arthur Andersen, Enron's auditor, underlining the importance of independent corporate governance and accurate financial reporting.

Bill Gallagher
There are no available Videos from "Bill Gallagher"

