Constructing Climate Hedge Portfolios

Robert Engle
Nobel Prize winning economist
In this video collaboration with MMF, Nobel Laureate and economist Robert Engle outlines how to construct a climate hedge portfolio using two strategies and explores why it's not that easy to hedge physical risks.
In this video collaboration with MMF, Nobel Laureate and economist Robert Engle outlines how to construct a climate hedge portfolio using two strategies and explores why it's not that easy to hedge physical risks.

Constructing Climate Hedge Portfolios
11 mins 11 secs
Key learning objectives:
Learn how to construct climate hedge portfolios
Define the characteristics of a stranded asset portfolio and a factor mimicking portfolio
Understand why fossil fuel energy stocks are rising
Define why it’s difficult to hedge physical risks
Overview:
Robert Engle shows us numerous strategies for constructing a climate hedge portfolio and their respective benefits. Robert then explores why it’s hard to hedge physical risks, the part of climate change most people worry about, and why the demand for oil and coal is going up.
What is a stranded asset portfolio?
This means going long on the S&P 500 and short 70% of the returns on a coal ETF and 30% of the returns on energy. This is all on energy stocks so it will presumably do well when energy stock prices are going down, and badly when they're going up.
What is a factor mimicking portfolio?
This means forming dynamic long-only portfolios of publicly available funds, minimising the variance of the portfolio and maximising the correlation of this portfolio with a news series. Then hold it for a month and then recalculate.
Why is it difficult to hedge physical risks?
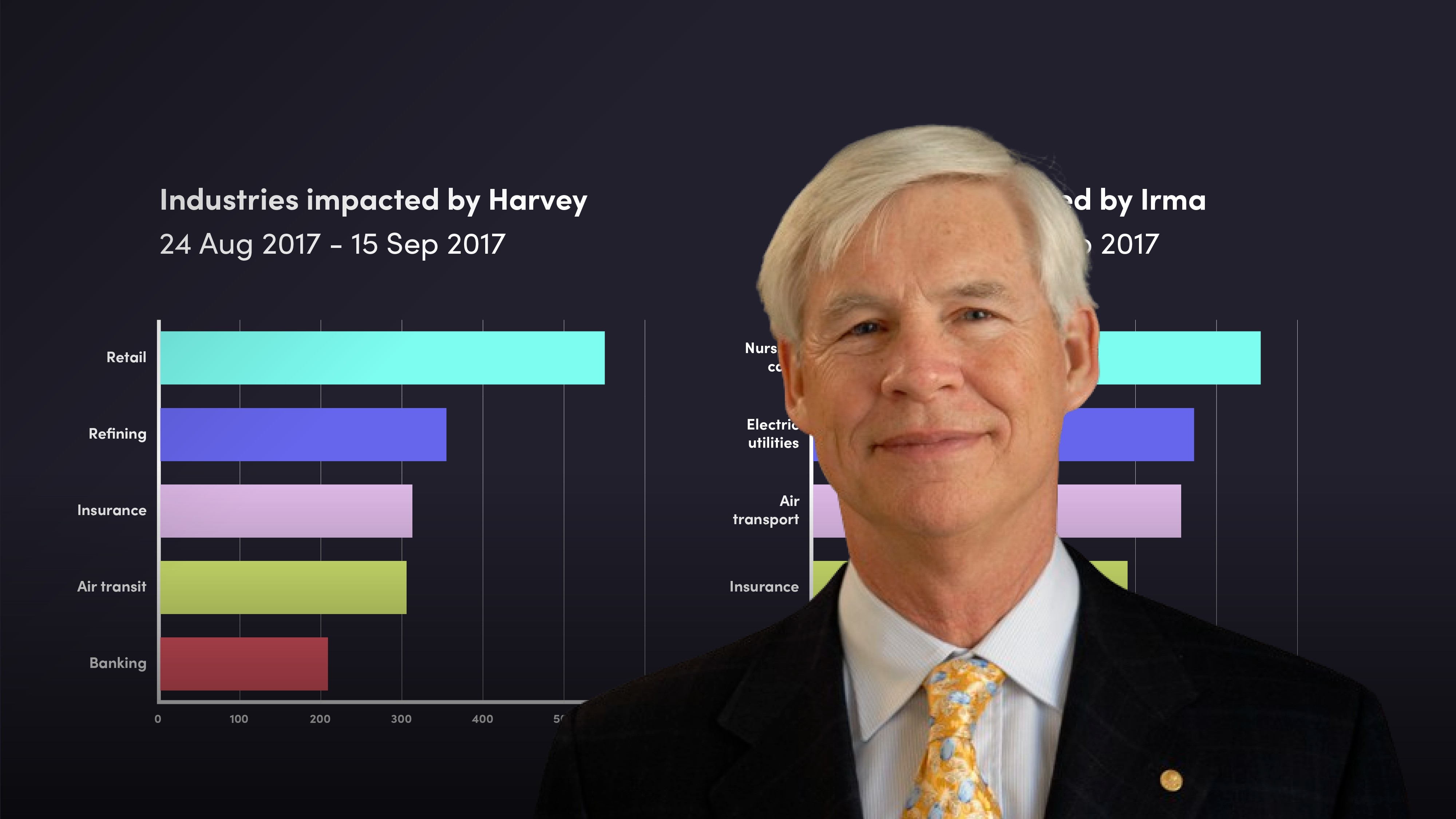
Climate physical risks, such as temperature change, drought, storms and wildfires is difficult to hedge because physical risks have to be geo-coded and stocks aren't particularly localised - although they have localised supply chains, plants or business models which are exposed to climate change.
Using two hurricanes in 2017 as an example, Hurricane Harvey had its biggest impact in retail, refining, insurance, air transit and banking. Hurricane Irma had its biggest impact on nursing care, electric utilities, air transport, insurance and tourism. So two separate hurricanes hitting similar locations in the US had completely different impacts across industries.
Why are fossil fuel energy stocks rising?
The demand for oil and coal is going up. One explanation for this is if the transition is done through regulation, it reduces the quantity of emissions but leads to higher and higher prices of energy stocks, akin to a carbon tax.

Robert Engle
There are no available Videos from "Robert Engle"

