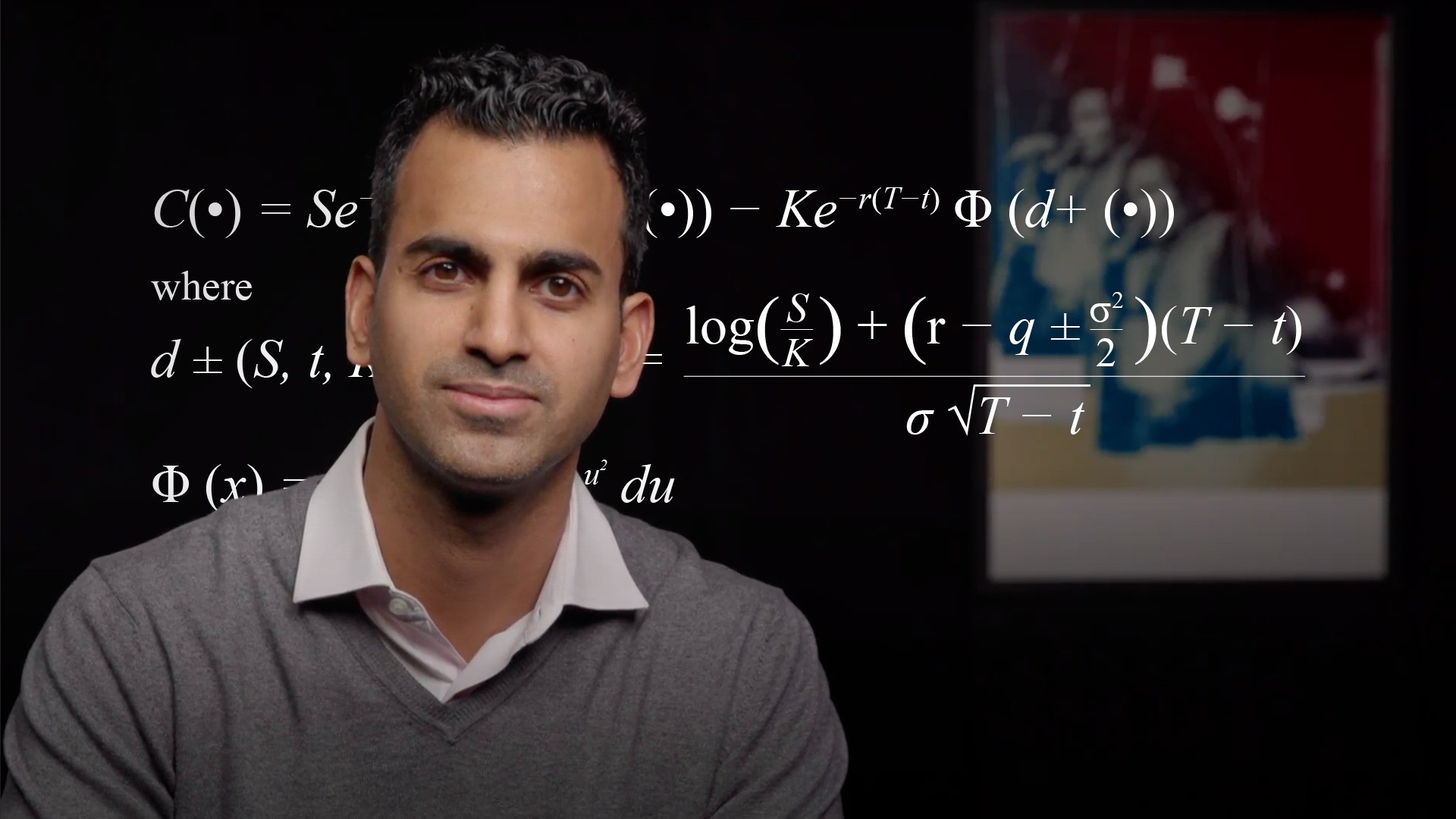
Equity Options Vega and Implied Volatility

Imran Lakha
20 years: Equity derivatives trading
In this video, Imran explains the meaning of implied volatility and how we can use the BS model to extract it from market option prices. He further discusses how vega is the greek exposure that an options price has to this implied volatility level and finishes with describing structure of volatility and how it can be used to derive forward volatility.
In this video, Imran explains the meaning of implied volatility and how we can use the BS model to extract it from market option prices. He further discusses how vega is the greek exposure that an options price has to this implied volatility level and finishes with describing structure of volatility and how it can be used to derive forward volatility.
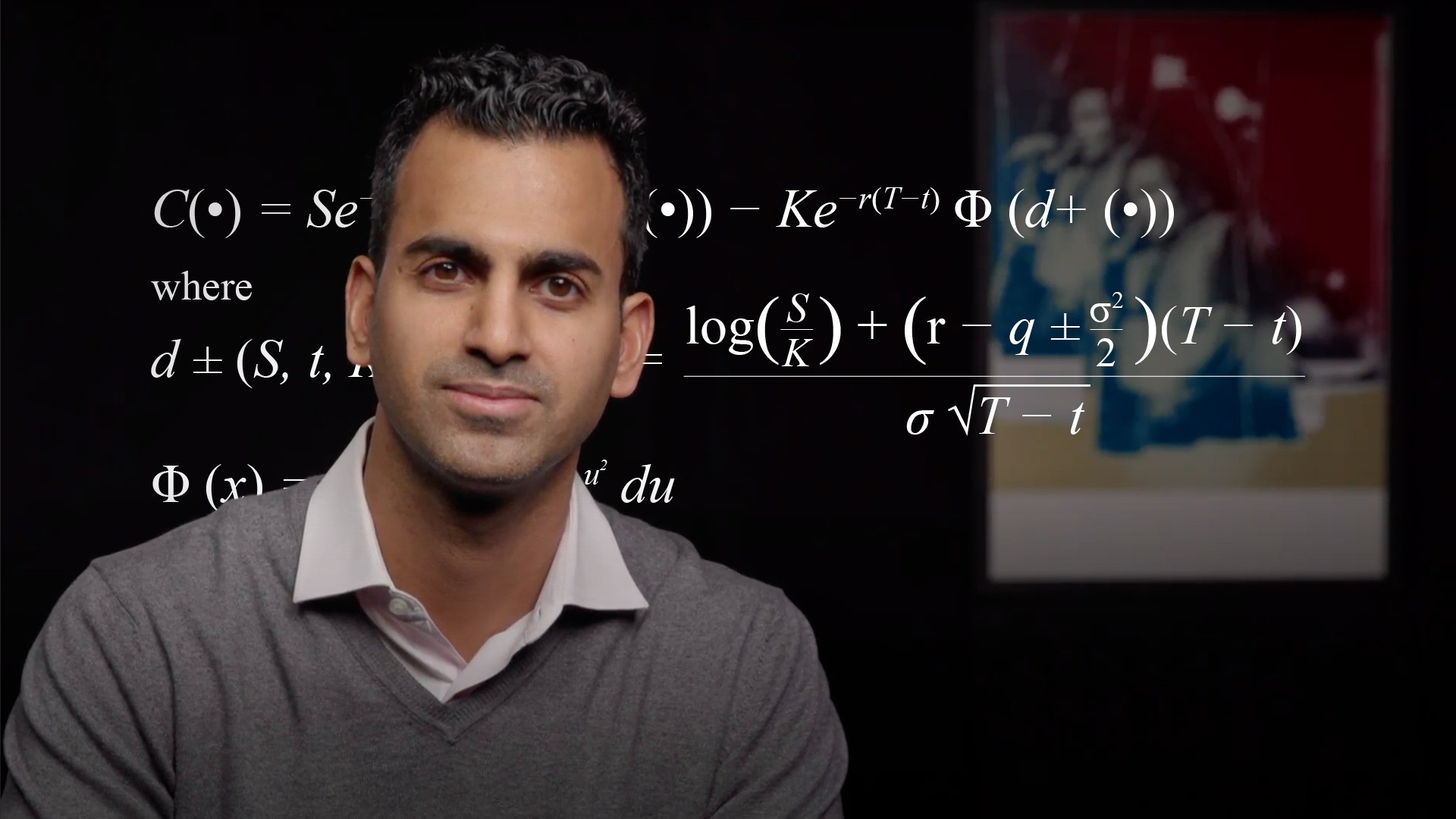
Equity Options Vega and Implied Volatility
13 mins 29 secs
Key learning objectives:
Define Implied Volatility and how is it extracted from market option prices through Black-Scholes model
Describe Vega & term structure of volatility
Understand how to calculate weighted vega
Define Forward Volatility
Overview:
When there is a significant event on the calendar, such as an election, the forward volatility that can be extracted from the term structure for a time span that captures the event is often elevated. This creates "kinks" in the volatility curve, which traders often buy or sell based on their expectations for the amount of volatility that the event would generate.
What is Implied Volatility?
Implied Volatility of an option is the market’s expectation of future realised volatility of the underlying equity up to a given maturity.
How do we use the Black-Scholes model to extract implied volatility from market option prices?
The Black-Scholes formula allows us to convert a fair option price, which is determined from the market by aggregating all buyers and sellers, into an annualised volatility which we call the implied volatility. We can 'imply' the volatility because the other inputs to the model are known and so the only unknown is the volatility which we can then solve for to arrive at our desired option fair value.
What is Vega & term structure of volatility?
Vega is the shift in option value caused by an increase in implied volatility of 1% or 1 vol point. You are Long Vega if you are long an option. As the implied volatility increases, the time value increases and the option gains in value. If the implied volatility went down to zero, the option would lose all its time value and be only worth its intrinsic value (if it had any).
We can trade options of many different expiries. These different expiries or maturities do not have to be priced on the same implied volatility for any given asset. We can see that implied volatility has a term structure, similar to a yield curve in interest rates, when we plot vol on the y-axis and maturity on the X-axis. The shape of that term structure can vary depending on market conditions.
How do we calculate weighted vega?
Because of the way the variable of time appears in the BS model, we infer that the acceptable weighting factor to use is 1/sqrt(T), where T is maturity in years. It is also the market convention and accurately reflects how we observe volatility surface changes on a daily basis.
What is Forward Volatility?
It is the implied volatility for a specific period of time in the future between two points on the curve.

Imran Lakha
There are no available Videos from "Imran Lakha"

