Introduction to Equity Options

Imran Lakha
20 years: Equity derivatives trading
In the first video of his series, Imran explains the two basic forms of stock options i.e. CALLS and PUTS along with how you can merge them to create a whole bunch of various payoffs. He has also addressed their most popular business applications and the motivations that influence their supply and demand.
In the first video of his series, Imran explains the two basic forms of stock options i.e. CALLS and PUTS along with how you can merge them to create a whole bunch of various payoffs. He has also addressed their most popular business applications and the motivations that influence their supply and demand.

Introduction to Equity Options
8 mins 11 secs
Key learning objectives:
Understand the two basic option types
Understand the concept of “ATM”, “OTM” and “ITM”.
Define Call options
Define Put options
Overview:
Options allow you to take a view not just on the direction of a market, but also the volatility and timing of the moves that you anticipate. Mastering options allows a trader to play in multiple dimensions as opposed to just focusing on the direction of the underlying.
What are the two basic types of options?
- Call Option
- Put Option
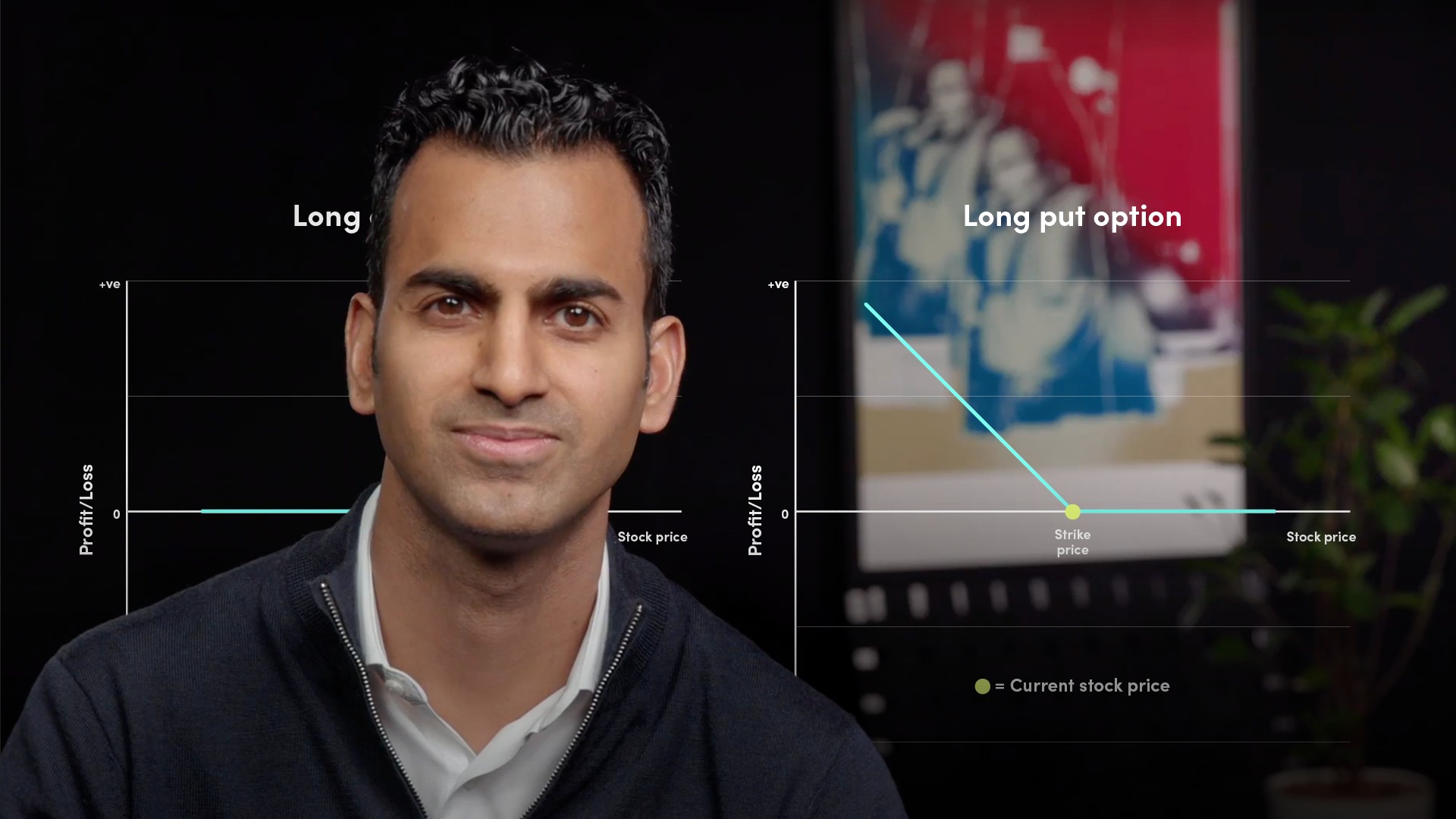
What is “ATM” , “OTM” and “ITM”?
Options have a STRIKE price at which you have the right to buy or sell the underlying stock if the option is exercised. If the STRIKE is the same as the current stock price, an option is said to be “At the money” (or ATM). If the STRIKE price is away from the current stock price such that the option would not be exercised, then it is called “Out the money” OTM. Finally, an option with a strike away from the current spot but which would be exercised is called “In the money” (ITM).
What are Call Options?
The right, but not the obligation, to buy an underlying asset for a fixed price, at a given maturity or expiry date. In equities, the most popular use for call options is to sell them against existing stock positions to earn income.
What are Put Options?
The right, but not the obligation, to sell an underlying asset for a fixed price, at a given maturity or expiry date.

Imran Lakha
There are no available Videos from "Imran Lakha"

