UK Insurance Regulators & Solvency II

Ted Wainman
20 years: CA & educator
The regulation of insurance companies has developed from the FSMA 2000 to the concept of ‘twin peaks’ regulation in 2010. Today the responsibility for regulation is split between the FCA (Financial Conduct Authority), the PRA (Prudential Regulation Authority) and the FPC (Financial Policy Committee).
The regulation of insurance companies has developed from the FSMA 2000 to the concept of ‘twin peaks’ regulation in 2010. Today the responsibility for regulation is split between the FCA (Financial Conduct Authority), the PRA (Prudential Regulation Authority) and the FPC (Financial Policy Committee).

UK Insurance Regulators & Solvency II
10 mins 46 secs
Key learning objectives:
Understand the ‘twin peaks’ of regulation in financial services
Outline the roles of the FCA, the PRA and the FPC
Define Solvency II
Overview:
As an essential element of the world of financial services, insurance companies are subject to strict regulatory governance in order to ensure their continuity and limit the risk of a major failure having a systemic impact on the system. In 2010 the UK regulatory landscape was changed with the implementation of the ‘twin peaks’ of governance by the Bank of England and the UK Treasury. Today the regulatory responsibilities are split between the FCA, PRA and the FPC.
What are the ‘twin peaks’ of regulation in financial services?
The Financial Services and Markets Act 2000 was replaced in 2010 with regulation being split between the Bank of England and the UK Treasury – known as the ‘twin peaks’.
What is the role of the FCA, the PRA and the FPC?
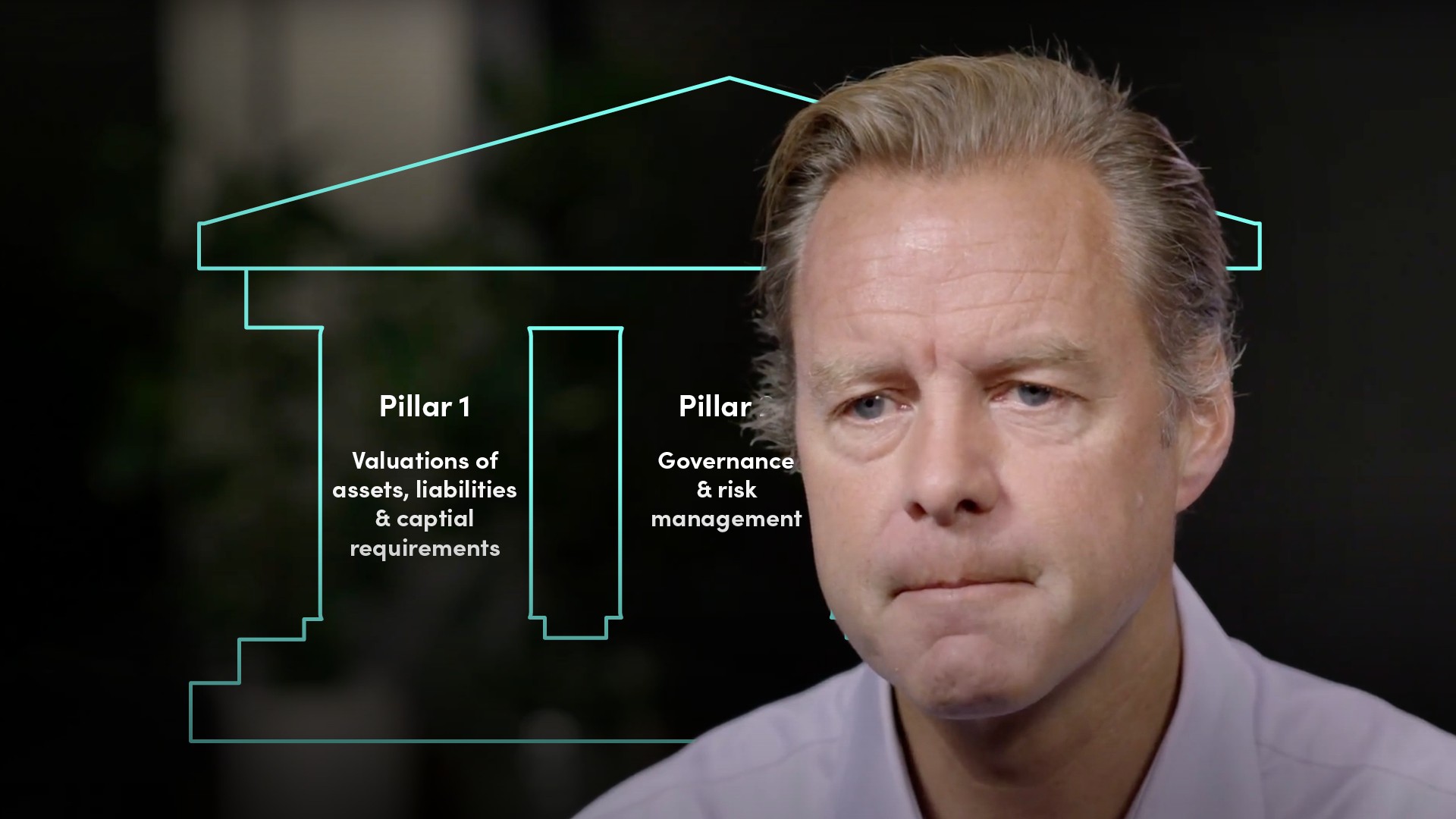
The Financial Conduct Authority is responsible for regulating the conduct of individuals within firms (Conduct of Business). The Prudential Regulation Authority is responsible for the financial soundness of significant firms (micro-prudential regulation). The Financial Policy Committee is responsible for the stability of the financial system as a whole (macro-prudential regulation and the systemic risk of the financial system).What is Solvency II?
Solvency II refers to the regulations surrounding the strength of an insurance company’s balance sheet. The regulation focuses on ‘three pillars’, being: the valuation of assets, liabilities & capital requirements; the governance and risk management; and reporting & disclosure.

Ted Wainman
There are no available Videos from "Ted Wainman"

