Introduction to Insurance Funding and Capital Ratings II

Gurdip Dhami
25 years: Treasury & ratings
In this video, Gurdip describes the general instrument features that the rating agencies review to assign ratings to instruments issued by insurance companies. He further introduces the three tiers of capital which make up solvency capital and provide some general guidelines on their rating levels.
In this video, Gurdip describes the general instrument features that the rating agencies review to assign ratings to instruments issued by insurance companies. He further introduces the three tiers of capital which make up solvency capital and provide some general guidelines on their rating levels.

Introduction to Insurance Funding and Capital Ratings II
9 mins 7 secs
Key learning objectives:
Understand how rating agencies assess subordinated debt and hybrid capital ratings
Outline the three tiers of capital that make up solvency capital
Overview:
In this video, Gurdip describes the general instrument features that the rating agencies review to assign ratings to instruments issued by insurance companies such as subordinated debt and hybrid capital. He also introduces the three tiers of capital which make up solvency capital and provide some general guidelines on their rating levels compared to senior unsecured debt.
What is Hybrid capital?
Hybrid capital generally refers to an instrument that has characteristics of both debt and equity, and therefore excludes common equity.
What is a credit rating?
A credit rating is a measure of the relative credit worthiness of an entity or instrument such as a corporate bond, so the rating of an instrument issued by an insurance company will depend on (1) whether it is issued by the operating company or holding company, (2) features such as its level of subordination, whether interest can be deferred, whether it is secured and whether it converts into equity or its principal can be written down due to a trigger event and (3) the duration of the bond for example whether it is perpetual or dated and (4) the legal form and regulatory framework.
Why do insurance companies issue subordinated and hybrid debt?
- They provide regulatory and rating agency capital
- They are cheaper and more flexible alternatives to equity
- The more equity like the instrument, the more credit the regulators and rating agencies will give insurers in their calculations of capital adequacy
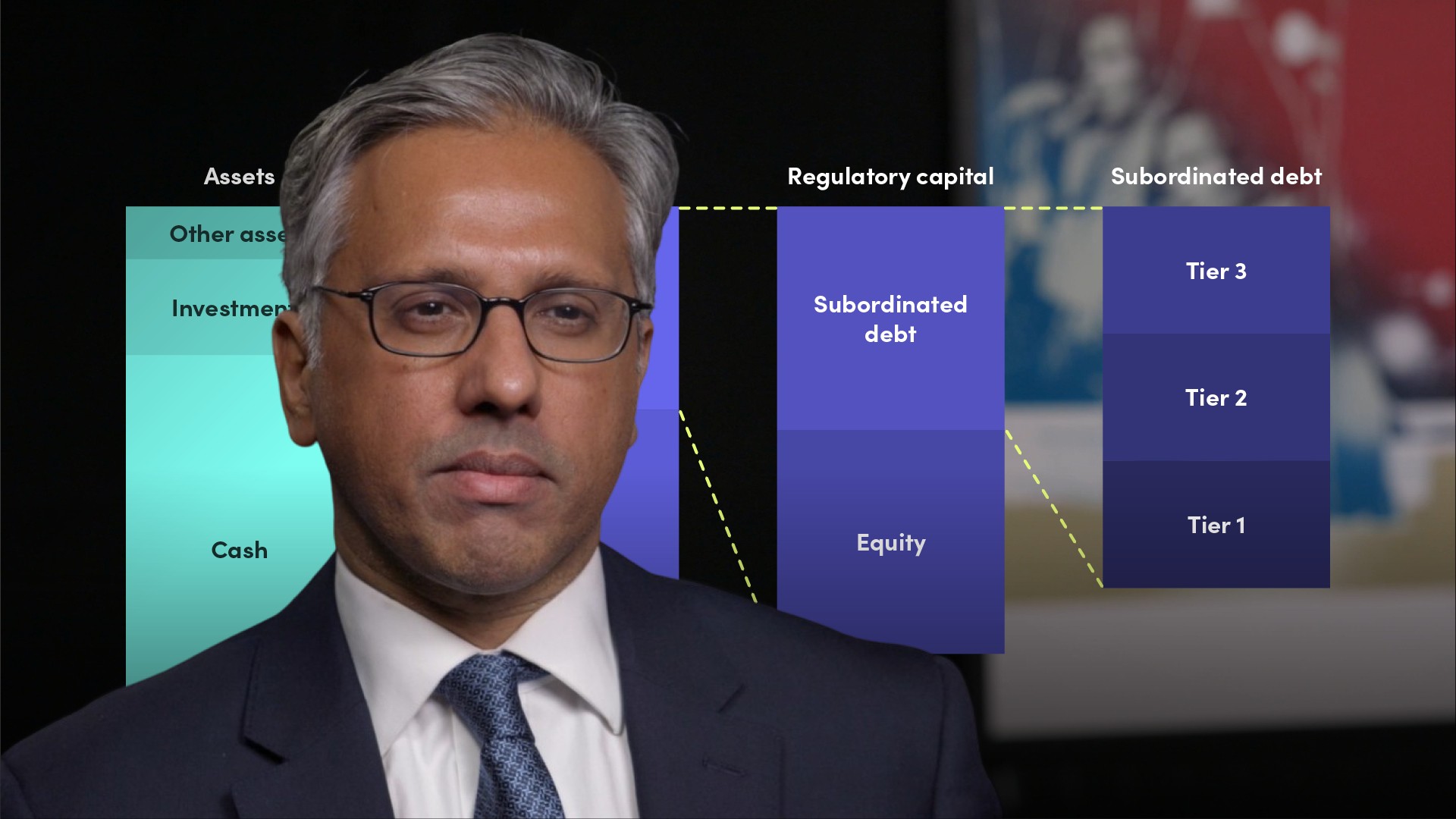
What are the three tiers of capital which make up solvency capital?
Insurance regulators in Europe divide solvency capital into 3 tiers depending on how equity-like they are - that is based on their permanency and ‘loss absorption’ ability. The three tiers are called Tier1, Tier 2 and Tier 3 and they have to have certain features to qualify as Solvency 2 capital, which are set out in regulation which can be found on the websites of regulatory authorities. Tier 1 capital is a higher quality capital than Tier 2 and Tier 3, and Tier 2 is higher quality than Tier 3. There are limits on how much capital can be in the form of the 3 tiers of capital: Tier 1, Tier 2 and Tier 3
How can notching vary from agency to agency?
In May 2020, Aviva Plc issued £500m of Tier 2 bonds which were rated by Moody’s and Fitch as A3 and BBB+ which is 1 and 2 notches respectively below the senior unsecured debt ratings. The Tier 2 bonds are dated with a maturity of approximately 35 years, subordinated to senior unsecured creditors of Aviva Plc and have optional and mandatory interest deferral. Both Moody’s and Fitch examine the features of the Tier 2 bonds and compare these to the guidelines in their criteria for hybrid capital to determine the rating of the Tier 2 bonds. In particular they review the level of subordination compared to senior unsecured bonds and interest deferral features including whether interest is cumulative or not.
In February 2018, Just Group PLC issued £230 million of seven year Tier 3 bonds with a Fitch rating of BBB which is 2 notches below the implied senior unsecured rating. The 2 notches reflected the subordination and loss absorption features of the bonds which contained mandatory redemption and mandatory deferral requirements triggered by breach of solvency requirements.
In June 2020, Legal and General Group Plc issued Restricted Tier 1 notes which were rated by S&P as BBB which is 3 notches below the senior unsecured debt rating of the holding company. The notes were rated as Baa3 by Moody’s which is 4 notches below the senior unsecured rating.

Gurdip Dhami
There are no available Videos from "Gurdip Dhami"

