Introduction to Agriculture and the Global Food System

Oliver Knight
15 years: Agricultural specialist
“However much food we produce, we always seem to want more.” This quote by economist Thomas Robert Malthus sets the scene for this introductory video on agriculture. Watch Oliver Knight as he guides us on what agriculture is, the context of agriculture and its main drivers.
“However much food we produce, we always seem to want more.” This quote by economist Thomas Robert Malthus sets the scene for this introductory video on agriculture. Watch Oliver Knight as he guides us on what agriculture is, the context of agriculture and its main drivers.

Introduction to Agriculture and the Global Food System
8 mins 42 secs
Key learning objectives:
Learn what agriculture is
Identify the 3 main drivers of agriculture
Understand how these 3 main drivers have led to significant climate costs
Overview:
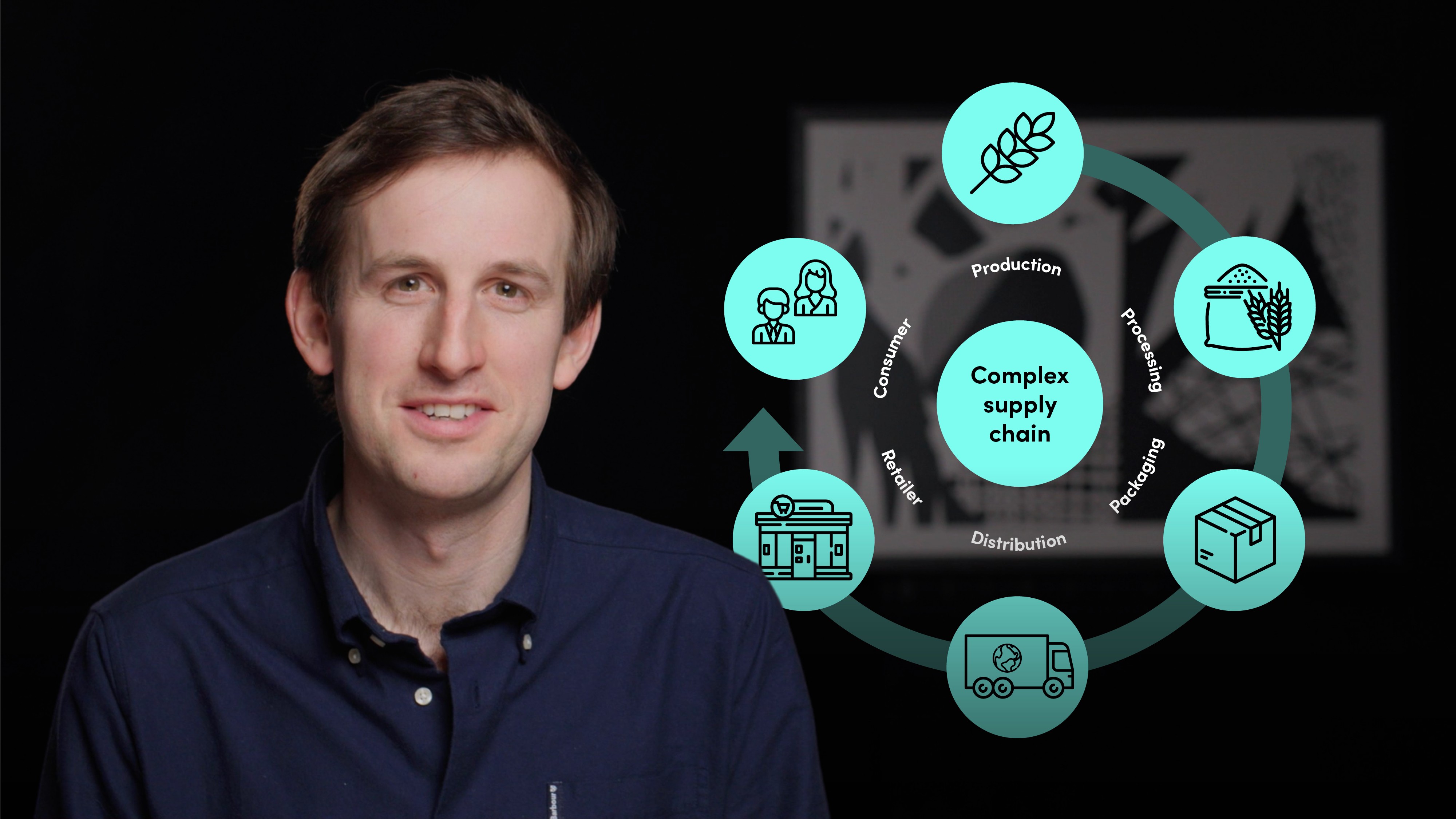
Agriculture is defined as the active production of useful plants or animals in ecosystems that have been created by people. The agricultural industry is the biggest and perhaps the most important sector in the world, keeping 300-350 million people employed and food stocked on shelves. It is also responsible for 30% of global emissions from farm to fork. Agriculture’s main drivers - maximising output, maintaining price stability and generating ever-cheaper food - have affected the climate significantly.
What is agriculture?
Agriculture is defined as the active production of useful plants or animals in ecosystems that have been created by people.
What is encompassed under the umbrella of agriculture?
Agriculture covers crop production (growing grains, cereals, grasses and pulses for human consumption, animal consumption and fuel) and livestock rearing. It also includes many related industries such as:
- Agronomy
- Horticulture
- Breeding and genetics
- Seed science
- Soil science
- Crop physiology
- Plant pathology
- Biotechnology
- Agricultural engineering
- Agricultural economics
- Agricultural chemistry
- Agricultural microbiology
Why is agriculture important?
Agriculture is the world’s largest employer, with an estimated 300-350 million small farmers globally. It is also central to communities, supporting livelihoods (particularly in rural areas), with a significant proportion of participation and employment fulfilled by women. It is also a central part of culture – food is one of our most basic needs and is a deep-rooted part of our identity.
Why do we need sustainable agriculture?
Agriculture is significantly exposed to (and a significant contributor to) climate change impacts. Changing climate, changing weather patterns and extreme events pose real challenges to the stability and sustainability of food production, particularly in areas already facing severe food security concerns.
Agricultural production is responsible for 11% of global emissions directly. When including related land use, land use change and forestry, the figure rises to 19% of global emissions (which is largely driven by deforestation for agricultural purposes). From farm to fork, the global food system as a whole is estimated to produce more than 30% of global emissions.
Likewise, it is both a contributor to and responsible for a large portion of the biodiversity losses we have faced over recent decades. The UN Environment Programme states that agriculture is the threat to 84% of the 28,000 global species at risk of extinction.
What are the 3 main drivers of agriculture?
Until recently, the overwhelming focus of the sector has been to:
- Maximise output
- Maintain price stability
- Generate ever-cheaper food

Oliver Knight
There are no available Videos from "Oliver Knight"

