Introduction to Cryptography

Ciaran Rooney
20 years: technology, cybersecurity & operations
Codes and ciphers are as old as time and have evolved throughout history. In fact, cryptography has advanced drastically in lockstep with computer technology. Join Ciarán Rooney as he explores cryptography, its history and the role of cryptography in modern communication systems.
Codes and ciphers are as old as time and have evolved throughout history. In fact, cryptography has advanced drastically in lockstep with computer technology. Join Ciarán Rooney as he explores cryptography, its history and the role of cryptography in modern communication systems.

Introduction to Cryptography
11 mins 48 secs
Key learning objectives:
Comprehend the history and evolution of cryptography
Identify the 2 main types of cryptography
Understand the main principles and roles of cryptography
Overview:
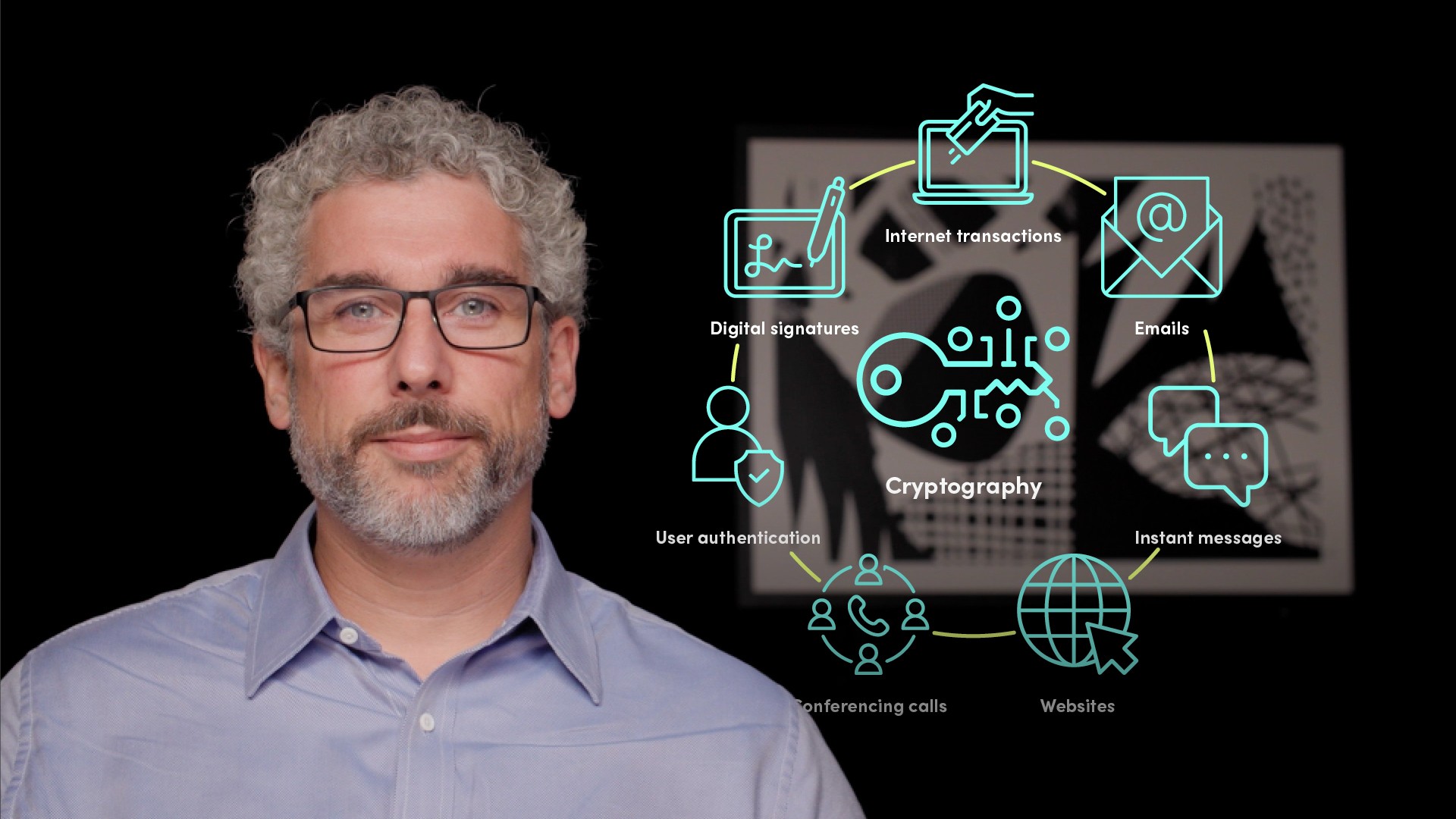
Cryptographic technology plays a crucial role in the security of the modern internet. It is used to encrypt and protect the content of all internet transactions, emails, instant messages, websites, and even conferencing calls. It is also increasingly used in areas such as user authentication and digital signatures.
What is cryptography and how did it originate?
Cryptography can be defined as the process of transforming ordinary text into unintelligible text and back again in order to secure a message so that only the sender and the intended recipient can view its contents. The earliest instances of cryptography are ancient Egyptian hieroglyphics, however, the most well known early form of cryptography was a simple substitution cypher called Caesar cypher used by Julius Caesar to safeguard military secrets.
What are the workings of a Caesar cypher?
- The sender encrypts their message by shifting every letter of the alphabet by left shift of three
- The recipient could then easily decrypt the message by aligning two alphabets by the known step
How has cryptography evolved through the decades?
As traditional methods had only a few techniques and combinations, it became easy for people to understand and decipher these types of classic cryptography through simple mechanical tools. Cryptography and computers have evolved together. During the early 1900s, complex mechanical and electromechanical machines provided more sophisticated and efficient means of encryption. Examples include machines used in WW2 such as the Enigma machine used by the Axis powers and the British bombe by Alan Turing designed to decrypt messages. In 1960’s, cryptography was primarily undertaken by governments for military purposes. Cryptography soon after attracted commercial attention, with businesses looking to secure their data from competitors and this was pioneered by IBM.
What are the main stages and principles of cryptography?
There are two main stages involved in any cryptographic process irrespective of application or type:
- Encryption - converting the information from a plain text to a cypher
- Decryption - sending the information and converting the cypher back into the original message
The four main principles of cryptography are:
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
- Non-Repudiation
- Authentication
What are the two main types of cryptography techniques?
Symmetric key cryptography - Also referred to as secret-key cryptography. The same encryption key is used for both encryption and decryption, hence it is called a Symmetric key. This is fast and simple but the problem is ensuring safe exchange of the key in advance.
Asymmetric key Cryptography - Also called public-key cryptography. A pair of keys (public key and private key) are used to encrypt and decrypt messages. The public key is used for encryption and the private key for decryption. Anyone may know the public key, the private key is known only by the receiver. This eliminates the security concern regarding the key exchange.

Ciaran Rooney
There are no available Videos from "Ciaran Rooney"

