Introduction to Data Science in Finance

Carlos Salas
Portfolio Manager and Data Scientist
Machine learning, artificial intelligence, supervised learning, clustering... there are a lot of data science terms and not much clarity. However, these concepts are becoming increasingly more common in our technological society. Join Carlos Salas as he breaks down what these concepts mean and their application in finance.
Machine learning, artificial intelligence, supervised learning, clustering... there are a lot of data science terms and not much clarity. However, these concepts are becoming increasingly more common in our technological society. Join Carlos Salas as he breaks down what these concepts mean and their application in finance.

Introduction to Data Science in Finance
11 mins 21 secs
Key learning objectives:
Understand what data science is
Identify applications for data science in finance
Understand the differences between key data science terms
Overview:
Data science can be defined as the process of building tools, systems and processes with the purpose of extracting insights from data. The financial world has been late to the party when it comes to embracing this tool but there have been adoption in areas such as: investment management, bespoke services, back-office operations, trade execution, economics research, fraud detection, client data and relationship management, real-time analytics, derivatives pricing, risk analytics, regulatory compliance.
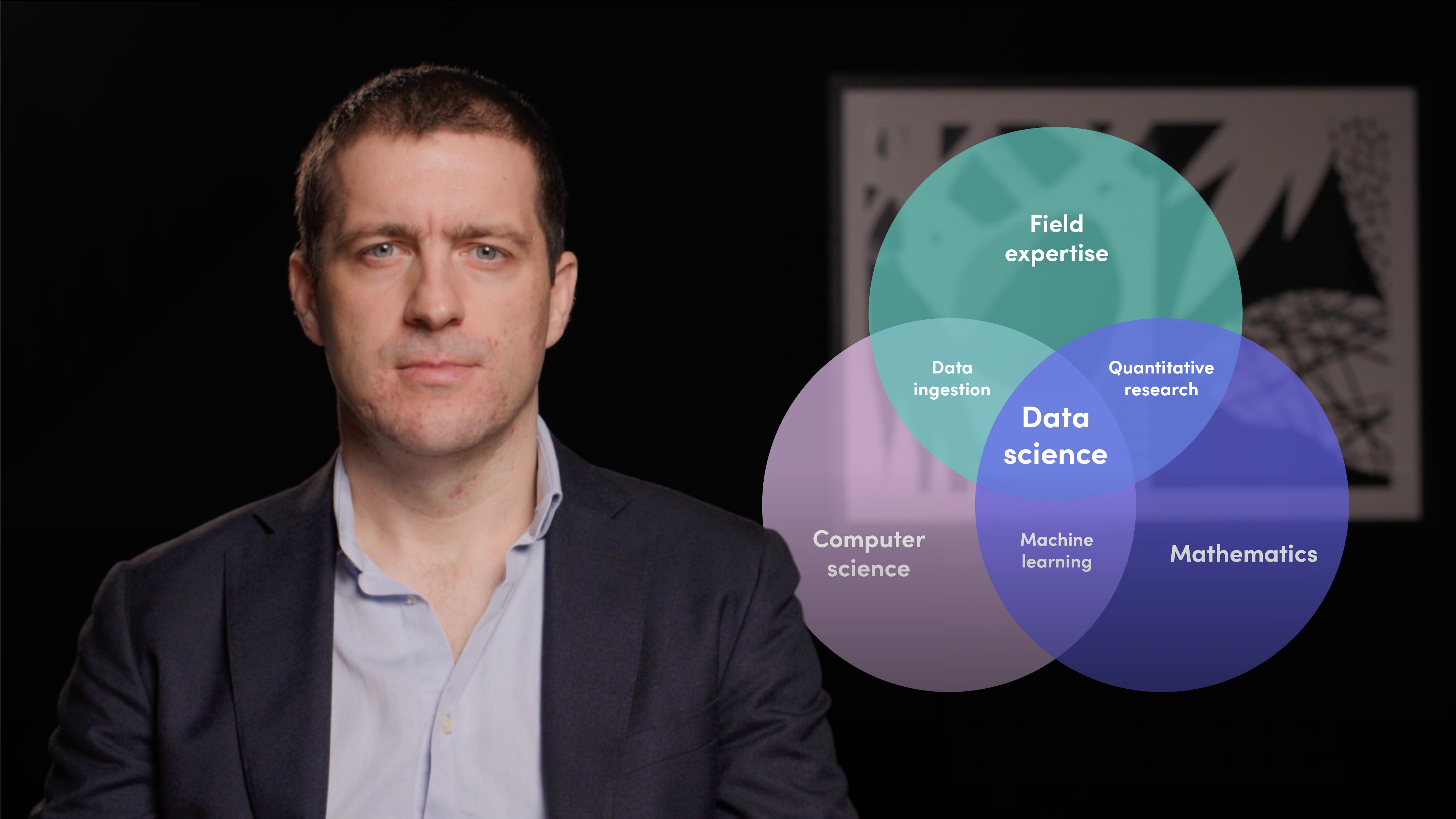
What is the definition of data science?
Data science can be defined as the process of building tools, systems and processes with the purpose of extracting insights from data. Data science is simply an analytical and computational process used to obtain relevant insights from data for a specific purpose.
What is the definition of artificial intelligence (AI)?
This is focused on teaching the machine to learn from the environment in order to complete complex tasks that would ordinarily require human-like capabilities and, eventually, become self-dependent for its own future growth.
What is the definition of machine learning?
Machine learning is a subset of AI that also seeks to train the machine to learn from its surrounding information, but to perform tasks that are more simple and restrictive in nature compared to those of AI.
What are important applications of data science and machine learning in finance?
1. Investment Management
There has been the use of enhanced tools for investment analysis and portfolio management, such as alternative data integration to complement traditional financial data, or the implementation of machine learning models to enhance portfolio optimisation and increase the robustness of investment strategies backtesting.
2. Bespoke Services
One example would be the secular trend of robo-advisors being used to offer a bespoke wealth management service for retail investors. Direct indexing is another bespoke niche consisting of customised indexation of portfolios based on investors’ specific investment criteria. .
3. Back-office Operations
This could include trade settlement automation and easy identification of failed and rejected trades. Machine learning can also allow back office officers to predict which trades may fail in the future based on the characteristics of past failures.
4. Trade Execution
This refers to the attainment of brand new superior levels of execution speed and efficiency in real time, as well as the ability to obtain alpha-generating insights from market movements.
5. Financial and Economics Research
Investment banks, along with central monetary policy institutions like the Fed, have now begun monitoring high frequency and alternative data. This data includes transcriptions, social media and online search trends, among others, and requires a heavy implementation of data science and machine learning techniques in order to produce useful insights.
6. Fraud Detection
Machine learning goes beyond a simple checklist of rules and allows users to identify fraudulent financial transactions via the implementation of anomaly detection algorithms. This tool also allows us too quickly and seamlessly access large datasets and to detect and flag irregularities on a timely basis.
7. Client Data and Relationship Management
This includes the encryption of data into more secure storage formats than local files in order to meet regulatory requirements such as GDPR.
8. Real-time Analytics
Chatbots are a good example of this area wherein AI is applied to Customer Relationship Management (CRM) in the financial sector. They can help to support both finance employees and their company’s clients.
9. Derivatives Pricing and Risk Analytics
Risk managers and derivative traders are now empowered to go beyond traditional finance assumptions, such as returns following a normal distribution, in favour of measuring risks and price derivatives using more realistic and empirically-grounded machine learning risk models. And lastly…
10. Regulatory Compliance
Data science and machine learning tools allow compliance officers to be better equipped to monitor and deal with public and private transactional data, in order to shortlist likely regulatory breaches, such as money laundering.
How has data science been impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic?
In a 2020 survey by the Bank of England, more than half of UK banks reported an increase in the importance of machine learning and data science as a result of the pandemic. Respondents also spoke favourably about the increasing role of machine learning and data science in the future of their operations.
What does the future look like for data science?
Current trends suggest that the number of employment opportunities in the data science and computer information research segment is expected to grow by more than 20% in the US this decade, with similar trends also expected globally. The majority of independent technology consultancy firms are forecasting double-digit annual growth rates for data science-related segments, such as machine learning, analytics, alternative data and big data solutions.

Carlos Salas
There are no available Videos from "Carlos Salas"

