Introduction to DEI

Arun Kelshiker
20 years: Asset management and stewardship
In this video, Arun Kelshiker provides an overview as to why DEI is crucial in today’s environment for companies, investors and society. Arun also covers six aspects of the DEI value chain from ensuring a DEI pipeline through to measuring DEI within organisations.
In this video, Arun Kelshiker provides an overview as to why DEI is crucial in today’s environment for companies, investors and society. Arun also covers six aspects of the DEI value chain from ensuring a DEI pipeline through to measuring DEI within organisations.

Introduction to DEI
18 mins 59 secs
Key learning objectives:
Understand the importance of DEI in today’s environment
Outline the six aspects of DEI value chain
Understand the regulatory aspects around DEI
Overview:
Recent events and movements have highlighted the importance of diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) in society. DEI strategies benefit both companies and investors, leading to better performance. Diversity includes various attributes, and equity focuses on fair access and support. Inclusion creates a respectful and engaged environment. DEI aims to build a diverse and inclusive workforce for a prosperous society. Institutions drive DEI through pipeline building, talent acquisition, promotion and retention, leadership, societal influence, and measurement. Regulatory bodies call for DEI disclosure, such as gender pay gap reporting. The gender pension gap is a significant challenge, with women receiving lower pension payments compared to men.
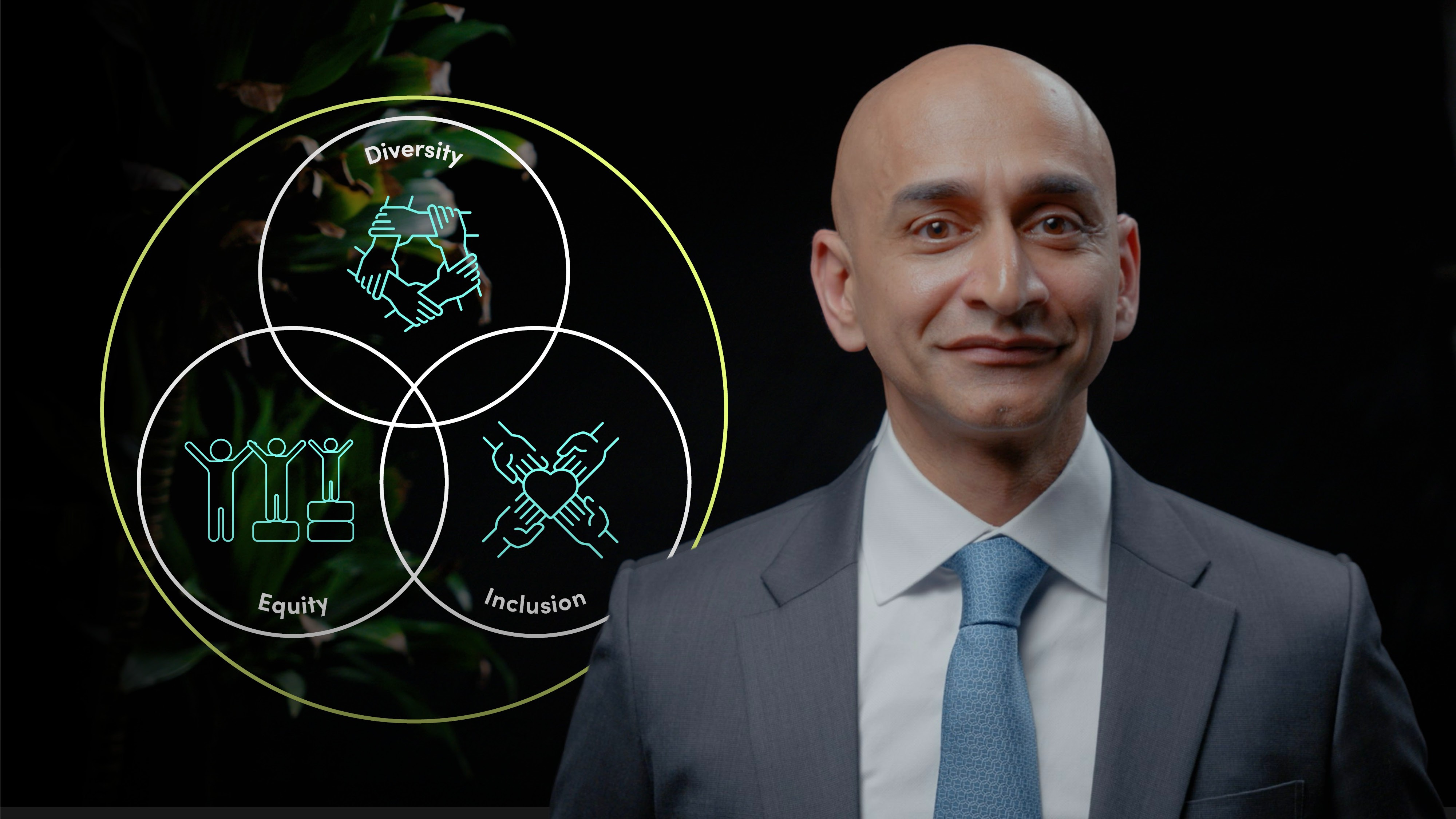
What is Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI)?
Values that organisations strive to embody to help meet the needs of people from all walks of life. Companies that are diverse, equitable and inclusive are often better positioned to respond to challenges, win top talent and meet the needs of a globally diverse marketplace.
What are some catalysts and trends that have contributed to the focus on diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) in recent years?
Some significant catalysts and trends include events like the murder of George Floyd and the rise of the Black Lives Matter movement, which have sparked conversations and actions on racial justice and equity. The "Me Too" movement has also exposed sexual harassment and assault within industries. Stakeholders are reassessing historical legacies tied to reprehensible practices such as slavery, leading to greater transparency and initiatives in academic institutions. These catalysts have driven the ambition for greater DEI in society. Additionally, research showing the business benefits of DEI, such as increased profitability and improved performance, has led to a dramatic increase in DEI strategies by corporations. Investors recognise DEI as a social responsibility and consider a company's DEI standing when making investment decisions.
How does DEI contribute to creating a positive work environment?
Diversity encompasses the representation of various attributes, perspectives, identities, and backgrounds in the workforce, including gender diversity, ethnic diversity, and individuals with physical and neurodiversity challenges. It also emphasises the importance of cognitive diversity, recognising the value of differences in thinking styles and problem-solving approaches.
Equity focuses on ensuring fairness of access, opportunity, and advancement for all employees by eliminating barriers that have hindered underrepresented groups from fully participating in the workplace. It acknowledges that individuals may have faced unique challenges and offers targeted support to help them reach their full potential.
Inclusion refers to creating an environment where every employee feels respected, valued, safe, and fully engaged. It involves embracing all employees, enabling them to make meaningful contributions and ensuring that their voices are heard.
What are the key components of the DEI value chain and how do they contribute to driving better DEI practices within organisations?
The key components of the DEI value chain are pipeline building, talent acquisition, promotion and retention, leadership, societal and industry influence, and measurement. These components work together to drive better DEI practices within organisations.
Pipeline building involves expanding a diverse talent pipeline by promoting role models from underrepresented groups and providing opportunities such as internships and industrial placements to increase awareness and interest in specific sectors.
Talent acquisition focuses on ensuring equitable and inclusive hiring practices at all levels. This includes providing anti-bias and cultural competency training for hiring managers, implementing blind applicant screening processes, and engaging with employee resource groups and business resource groups to support DEI ambitions.
Promotion and retention strategies aim to create inclusive and equitable opportunities for employees. This involves reviewing talent assessment, work allocation, and promotion processes for biases, implementing transparent and consistent opportunities, and offering mentorship and sponsorship programs to support career development.
Leadership plays a critical role in driving DEI outcomes. Organisations are appointing senior leaders dedicated to DEI integration, implementation, and measurement, holding them accountable for the organisation's DEI activities and standing.
Societal and industry influence refers to organisations leveraging their influence to encourage internal and external stakeholders, including employees, clients, and industry partners, to adopt DEI best practices. This can involve industry-wide collaboration and the establishment of voluntary codes, as seen in the financial services industry with the CFA Institute's DEI code.
Measurement is crucial for successful DEI strategies. Organisations employ systematic data collection frameworks and protocols to gather DEI metrics. These measurements provide a deeper understanding of DEI and help transform organisational culture by highlighting the importance of DEI to stakeholders.
How has the UK addressed gender pay gaps and what is the impact?
The UK requires companies with over 250 employees to report their gender pay gaps, highlighting the difference in average earnings between men and women. Since 1997, the gender pay gap in the UK has improved from 27.5% to around 8.3% in 2022. However, gender pay gaps can lead to further challenges, such as the gender pension gap, where women receive lower pension payments than men. Efforts to address these gaps aim to promote gender equality and financial security for women in retirement.

Arun Kelshiker
There are no available Videos from "Arun Kelshiker"

