Introduction to Greenhouse Gas Emissions

Gordon Rowan
20 years: Origination and Credit Structuring
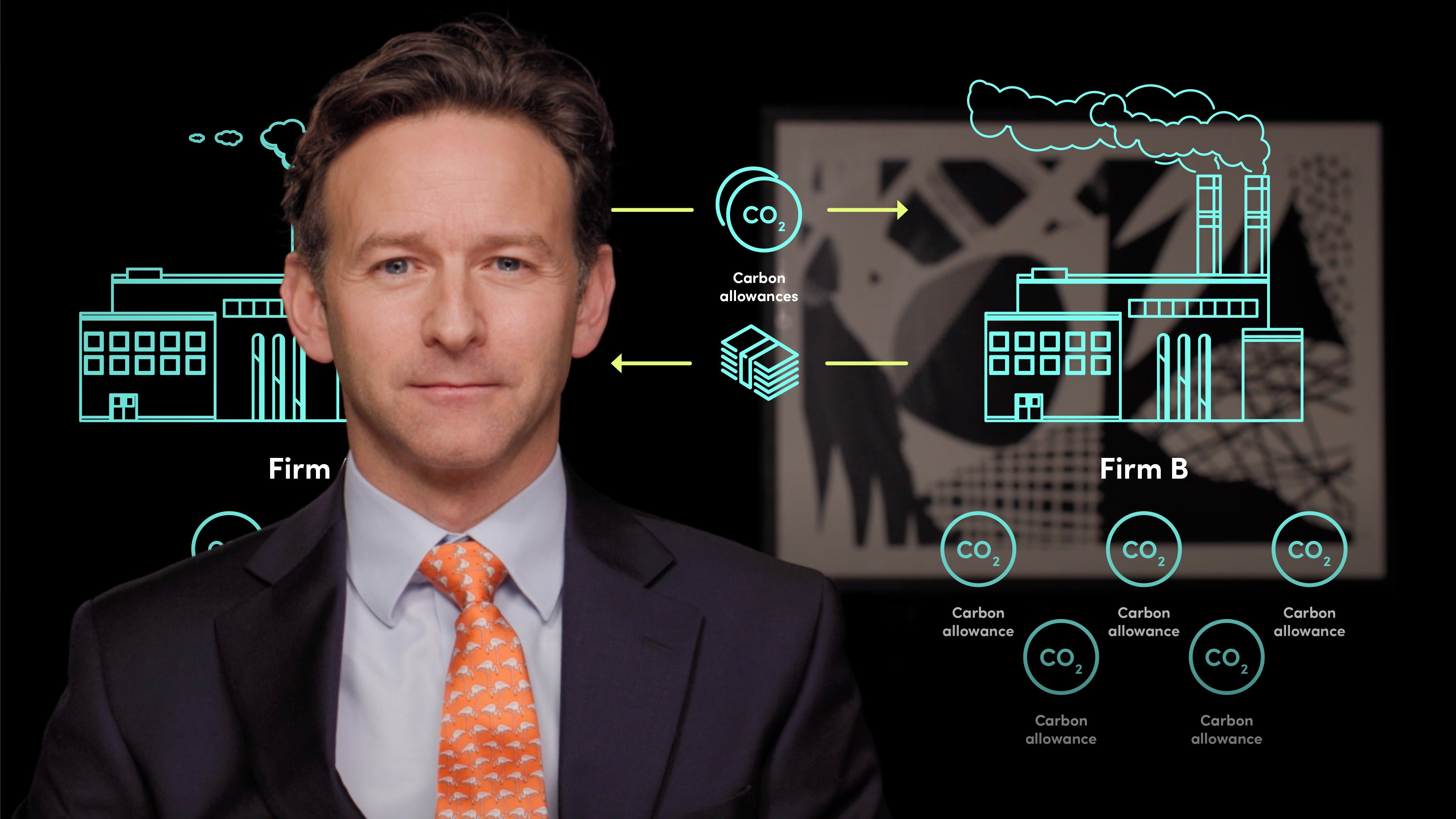
In this video, Gordon introduces the Keeling curve, the concentration of carbon in the atmosphere, and the idea that market-based tools such as cap and trade can help us to reorganise our economies to reduce the amount of CO2 being emitted into the atmosphere.
In this video, Gordon introduces the Keeling curve, the concentration of carbon in the atmosphere, and the idea that market-based tools such as cap and trade can help us to reorganise our economies to reduce the amount of CO2 being emitted into the atmosphere.

Introduction to Greenhouse Gas Emissions
7 mins 25 secs
Key learning objectives:
Understand what a concentration of 416 ppm mean
Understand the concept of greenhouse gases
Understand the government's initiatives to reduce carbon emissions
Overview:
By absorbing solar energy and reducing the speed at which it escapes into space, greenhouse gases warm the Earth by insulating it like a blanket. The warming of the Earth is influenced differently by various GHGs. The Global Warming Potential is a metric used to compare GHGs to the amount of energy that one tonne of CO2 will absorb over a century ("GWP"). Although CO2 has a GWP of 1 by definition, it can linger in the atmosphere for a much longer period of time than 100 years. The worst are chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and their relatives, whose GWPs are thousands or tens of thousands of times more than CO2 equivalent. This is due to the fact that they significantly capture more heat than CO2 for a given mass.
What does a concentration of 416 ppm mean?
When measuring gases (like carbon dioxide), the term "concentration" is used to describe the proportion of a gas by volume in the air. One part per million (by volume) is equal to one volume of a given gas in a million volumes of air:
So, here it’s: 416 / 1,000,000
How greenhouse gases warm the earth
- Absorbing energy from the sun
- Slowing the rate at which the energy escapes to space
What are the ways in which greenhouse gases differ from each other?
The two main ways in which these gases differ from each other are their ability to:
- Absorb energy (radiative efficiency)
- How long they stay in the atmosphere (lifetime)
How long do greenhouse gases stay in the air?
CO2 gas can actually stay in the atmosphere for thousands of years rather than 100 years
- Methane gas has a GWP of 28 to 36 times that of the CO2 equivalent. This is because methane absorbs much more energy than CO2 - but lasts about 10 years in the atmosphere.
- Nitrous Oxide has a GWP of 265- 298 times the CO2 equivalent and remains in the atmosphere for more than 100 years on average.
- The three main categories of Chlorofluorocarbons and their cousins are the worst - with GWPs thousands or tens of thousands of times the CO2 equivalent. This is because for a given mass, they trap substantially more heat than CO2.

Gordon Rowan
There are no available Videos from "Gordon Rowan"

