Liability Management in Practice

Sushanth Papireddy
15 years: Liability Management
In this video, Sushanth covers the actual workings of each of the liability management transactions. He then covers the economic risks and rewards of participating in these transactions and explains what drives bondholder participation in a liability management operation.
In this video, Sushanth covers the actual workings of each of the liability management transactions. He then covers the economic risks and rewards of participating in these transactions and explains what drives bondholder participation in a liability management operation.

Liability Management in Practice
6 mins 11 secs
Key learning objectives:
Understand the mechanics of bondholder consent solicitations, tender offers, and exchange offers
Outline the economic incentives and risks that drive bondholder participation in LM transactions
Overview:
LM mechanics for bondholder consent solicitations, tender offers, and exchange offers are governed by the terms of the bonds and associated agreements. Incentives and risks drive bondholder participation in these transactions, such as consent fees for solicitations and premiums to market price for tender offers. Non-participation risks losing out on these incentives, while the reduced liquidity from buying back bonds could discourage participation. When structuring LM exercises, companies must be careful not to use overly coercive structures to avoid pushback from investors and reputational risk. Precedent transactions can provide a guide to market conventions and outcomes.
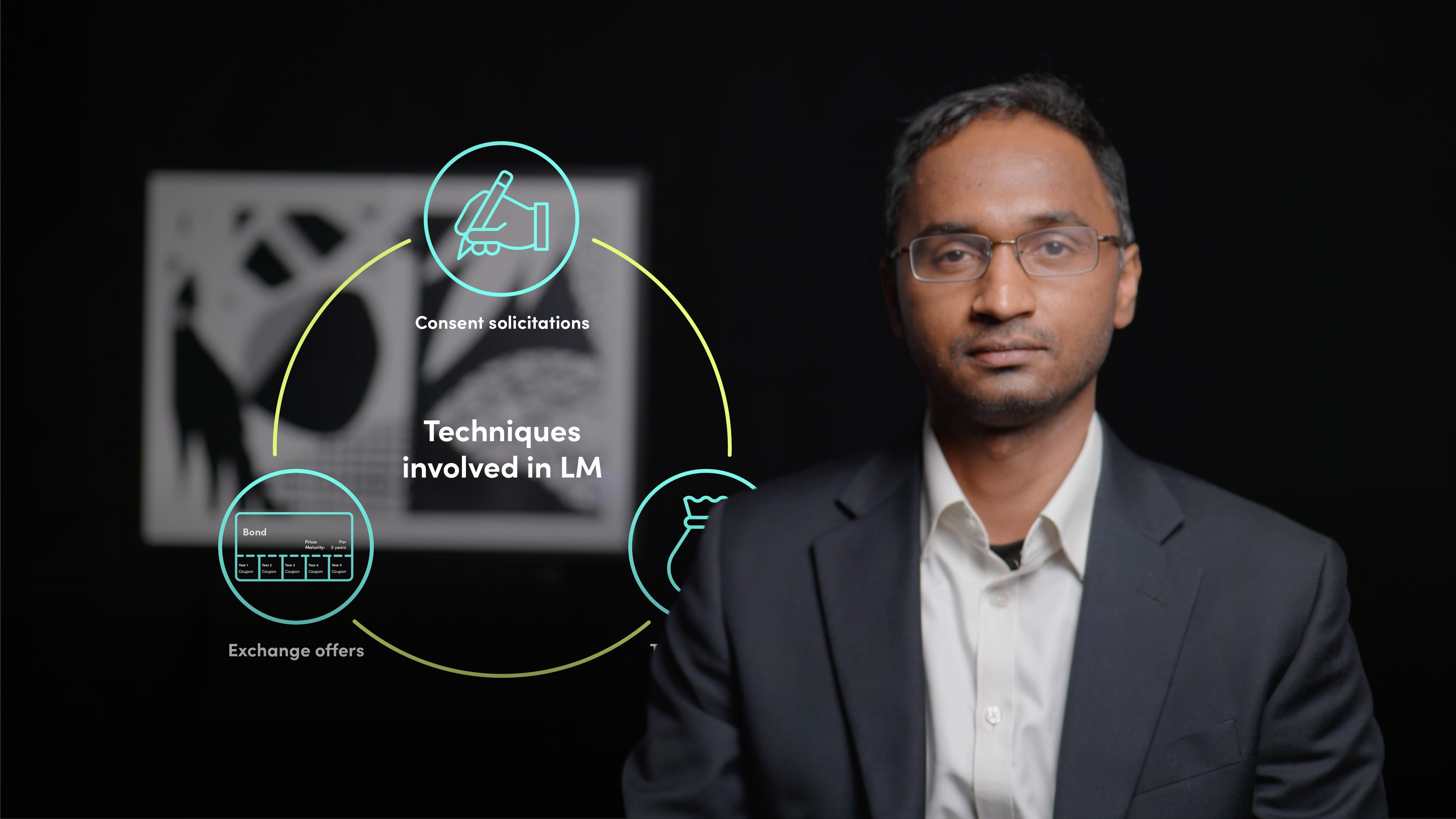
What are the mechanics involved in the different types of LM transactions?
The mechanics of different types of LM transactions involve various procedures and protocols. In consent solicitations, the terms of the bonds and agreements dictate the process for seeking noteholder consent. Bondholders are incentivised to vote in favor through the payment of fees.
Tender offers involve a public announcement by the company regarding its intention to buy back certain bonds, with buyback levels set at a premium to market levels prior to the LM announcement. The company can set a priority order for acceptance, and legal counsel and a tender agent must be engaged to produce the documentation and facilitate settlement.
Exchange offers are similar to tender offers, but instead of cash, bondholders receive new bonds with different pricing terms and specifications.
What drives bondholder participation in an LM exercise?
Bondholder participation in liability management (LM) exercises is primarily driven by economic incentives and risks associated with non-participation.
Consent fees and premiums offered in tender offers are common incentives, while the potential loss of consent fees or reduced liquidity can act as disincentives for non-participation.
Bondholder composition also influences take-up, with investors who prefer to hold bonds to maturity being less likely to participate in tender offers.
Careful consideration of incentives and disincentives is essential, as overly coercive structures can lead to investor pushback and reputational risk for the company. Precedent transactions can provide guidance on market conventions and outcomes of LM exercises.

Sushanth Papireddy
There are no available Videos from "Sushanth Papireddy"

