Private Equity Asset Class Performance

Gavin Ryan
25 years: Private equity & banking
Private equity performance statistics should always be analysed with some scepticism; because they are extremely unreliable and inconclusive. Gavin explains why this is the case by analysing the key performance metrics: Internal Rate of Return (IRR), Cash Multiple, Distributions to Total Value (DVTV) and Residual Value to Total Value (RVTV).
Private equity performance statistics should always be analysed with some scepticism; because they are extremely unreliable and inconclusive. Gavin explains why this is the case by analysing the key performance metrics: Internal Rate of Return (IRR), Cash Multiple, Distributions to Total Value (DVTV) and Residual Value to Total Value (RVTV).

Private Equity Asset Class Performance
11 mins 1 sec
Key learning objectives:
Outline the key performance metrics
Understand how PME works
Understand how VAA works
Overview:
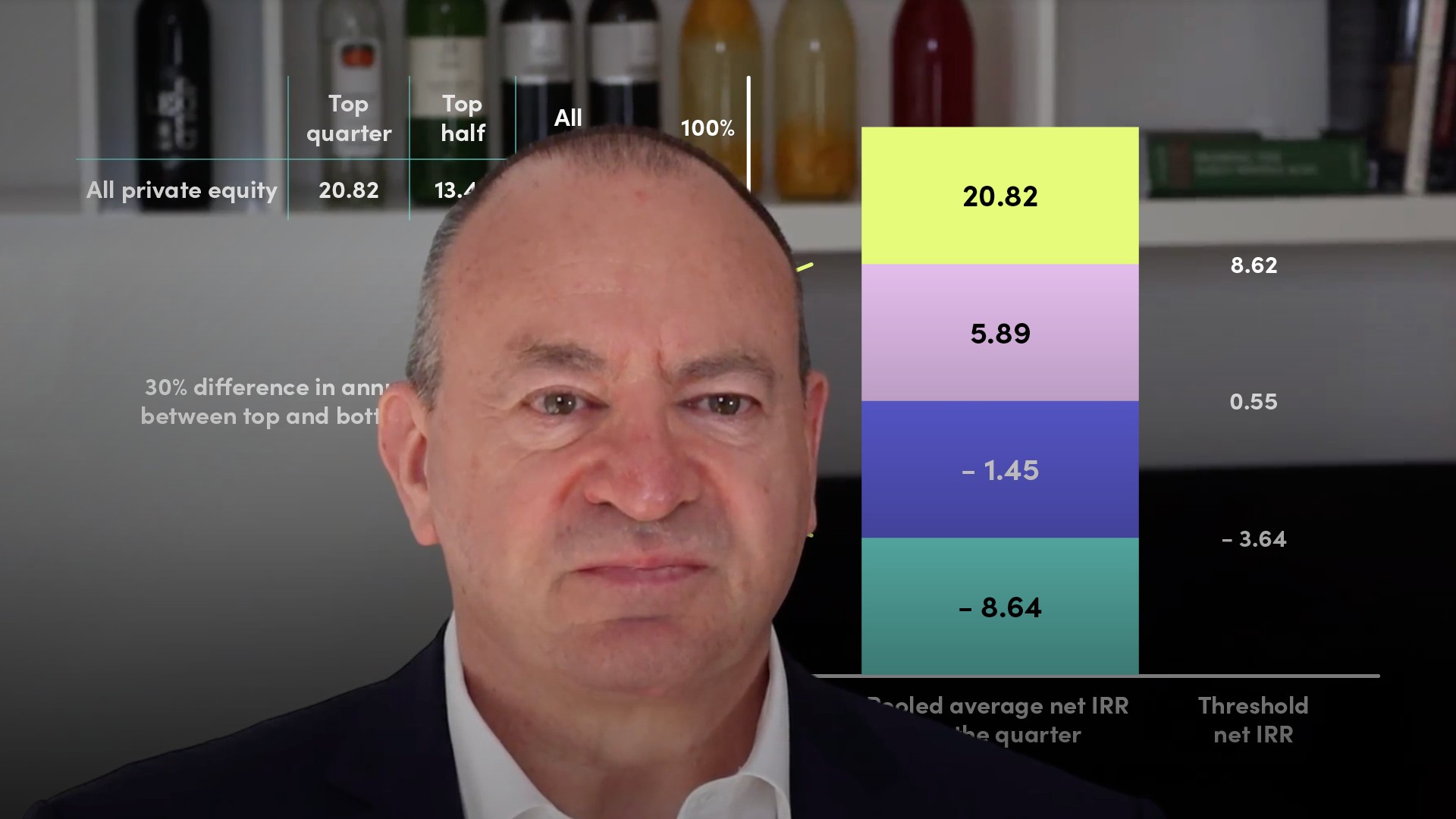
The private equity (PE) asset class is notoriously opaque, when it comes to divulging information about the performance of investments and funds. Private equity performance statistics should always be analysed with some scepticism. The two main methods to analyse private equity performance are the Public Market Equivalent method, which benchmarks against listed companies or an index; and Value Attribution Analysis, which traces the sources of value creation in an investment. Historically, the PE asset class has returned between 9 and 12% on average; and the top/bottom quartile spread is over 20%.
What are the key performance metrics?
Key metrics are Internal Rate of Return (IRR), Cash Multiple, Distributions to Total Value (DVTV), and Residual Value to Total Value (RVTV).
IRR has been criticised as a reliable measure because of the way it is calculated technically, which has the effect of amplifying positive investments upwards and negative investments downwards. Nevertheless, used in combination with other measures, it is still the most widely used metric.
One last technical distinction we need to make is Net IRR, the return received by limited partners (LPs) after the fund manager’s fees are deducted and Gross IRR, the return of the portfolio before fees are deducted.
How does Public Market Equivalent (PME) work?
Many LPs use PME to assess their PE portfolio. Academic studies also use this method. PME works by comparing a private equity investment to a comparable quoted company or stock market index. The method requires a lot of careful statistical adjustments.How does Value Attribution Analysis (VAA) work?
VAA looks at an individual investment and tries to break down how the value has been created, in order to get better insight into the portfolio. Value can be created by leveraging the company, by buying at a lower multiple than when selling and by growing earnings. Most investments’ value creation is a combination of these three factors and it is interesting to establish their relative weight.
Gavin Ryan
There are no available Videos from "Gavin Ryan"

