Introduction to Stock Exchanges

Peter Eisenhardt
30 years: Capital markets & investment banking
When you think of a marketplace for financial instruments, you probably immediately think of stock exchanges - the topic of this short.
When you think of a marketplace for financial instruments, you probably immediately think of stock exchanges - the topic of this short.

Introduction to Stock Exchanges
8 mins 35 secs
Key learning objectives:
Understand the origin and purpose of a stock exchange
Explain how bonds are traded and the reasons and implications of trading OTC
Identify the additional responsibilities of a stock exchange
Overview:
Stock exchanges were created as a venue for buyers and sellers to trade financial assets. As these exchanges became more sophisticated, the responsibility to ensure fair dealing, transparency, liquidity, validity, and routine disclosure of issuers have also been put on stock exchanges. Stock exchanges are the critical venue for equity trading, but not for the bond, derivatives, or foreign exchange markets.
How did stock exchanges first come into existence?
Joint-stock companies first came into prominence in the 17th century. Shares were issued on paper, and could be sold to other investors, but in London there was no stock exchange. Buyers and sellers ended up meeting at coffee houses to make trades, however, using coffee houses as stock exchanges meant there were no regulations on the issuance and trading of shares.
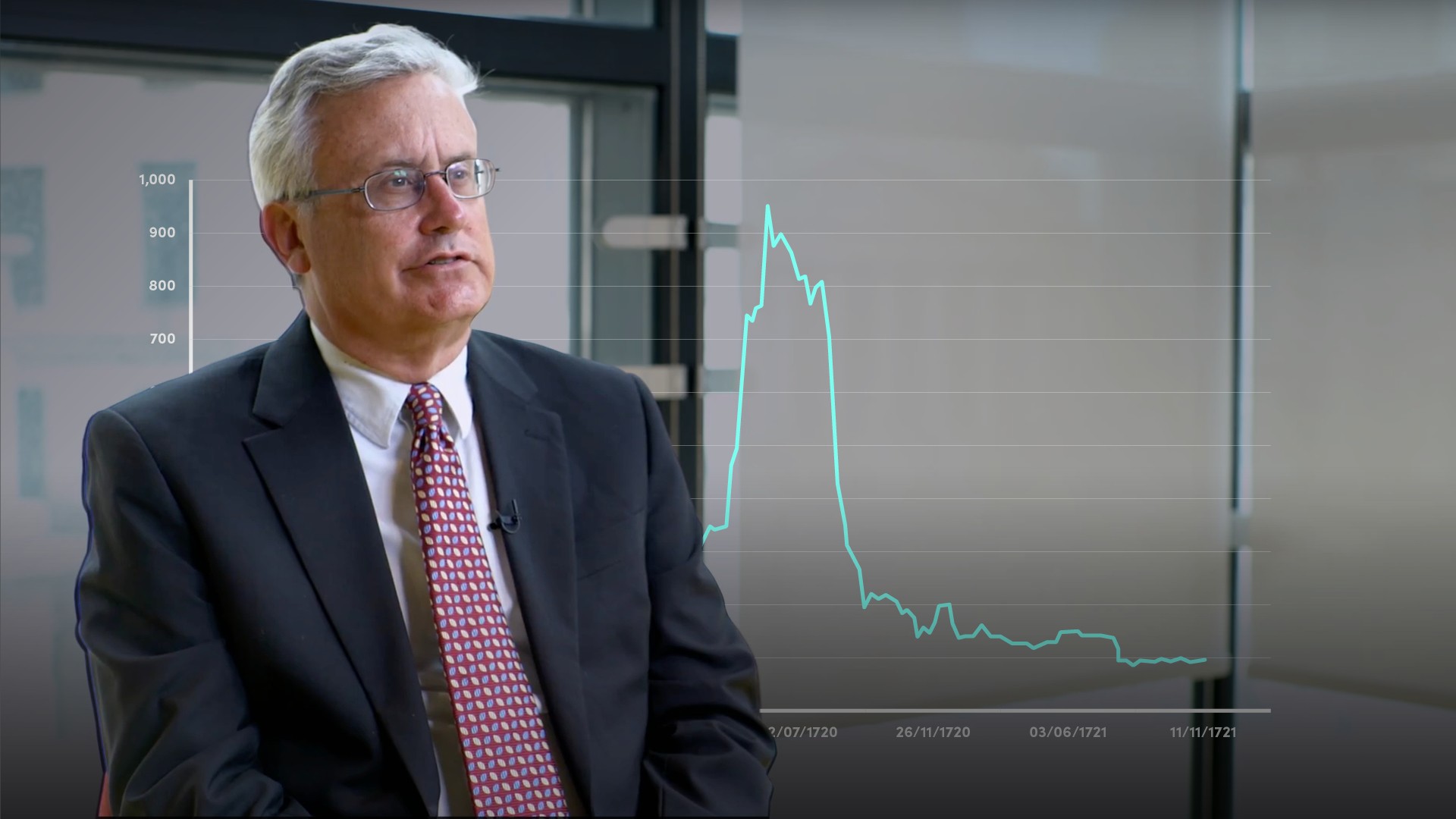
Ultimately, this unregulated, informal market hosted the South Sea asset bubble, which burst in 1720. As a result, the issuance of shares was actually banned in Britain until 1825.
What are the top ten stock exchanges?
The top ten exchanges by turnover are:
NYSE, NASDAQ, Tokyo, Shanghai, Hong Kong, Euronext, London, Bombay, Shenzhen, and Toronto.
What responsibilities have been put upon stock exchanges?
Stock exchanges are responsible for facilitating and supervising:
- Fair Dealing - Orders must be handled and trades must be executed under clearly defined rules
- Transparency - Prices and volumes must be reported accurately and on a timely basis to make for efficient price discovery
- Liquidity - Most exchanges have designated market-makers who are obliged to take the other side of trades when there are short-term buy and sell-side order imbalances. In exchanges, these specialists get information and trade execution advantages
- Security and Validity of Transactions - All participants must be verified and monitored so as to ensure they are able to meet the settlement obligations
- Listing - Listed companies must meet corporate governance standards and obligations, such as timely filing of financial reports and instant reporting of relevant developments
Are bonds listed on a stock exchange?
Yes, bond securities are often “listed” on a stock exchange which means investors draw comfort from the reporting and disclosure responsibilities this imposes on individual bond issuers, but the stock exchanges themselves don’t provide a formal venue for the trading of these securities.
What is Over-the-Counter trading?
Over-the-counter (OTC) trading is trading that usually takes place bilaterally and by appointment between the contracting parties without the intervention, facilitation or supervision of an exchange.
Why do bonds trade OTC rather than on a formal exchange?
There are more types of bonds issued than equity. As a consequence, most bonds are less liquid than most shares i.e. they trade less frequently.
What is a disadvantage for the bond market trading OTC rather than on an exchange?
The bond market is less transparent and price discovery is harder compared to the exchange-traded Equity market, where trades and prices are published instantly.
How are regulators trying to increase transparency within bond trading?
The US - In the US bond market, the Trade Reporting and Compliance Engine (TRACE) was introduced to encourage more transparency. TRACE is operated by the Financial Industry Regulation Authority (FINRA) and provides investors and market professionals with access to information on nearly all trading activity in corporate, agency and securitised bonds.
The EU - The EU has been working to improve bond market transparency through a piece of legislation called MiFID II, which is to provide more transparency on trading activity in OTC markets.
Which other markets do not trade on an exchange?
- Global derivatives market - The majority of these contracts trade OTC
- The foreign exchange market - It is the most liquid market in the world and is traded daily in a 24-hour OTC market

Peter Eisenhardt
There are no available Videos from "Peter Eisenhardt"

