
The Role of a Bank's Asset-liability Committee (ALCO)

Moorad Choudhry
35 years: Banking and Capital Markets
A bank’s Asset-Liability Committee or ALCO is possibly the most important executive operating committee in a bank. Here, Moorad explains what ALCO is, outlines their responsibilities and provides some insight into their objectives and governance structure.
A bank’s Asset-Liability Committee or ALCO is possibly the most important executive operating committee in a bank. Here, Moorad explains what ALCO is, outlines their responsibilities and provides some insight into their objectives and governance structure.

The Role of a Bank's Asset-liability Committee (ALCO)
11 mins 28 secs
Key learning objectives:
Define an ALCO
Outline the main responsibilities of an ALCO
Understand what the ideal ALCO governance structure looks like
Overview:
The role of a bank’s Asset-Liability Committee ultimately lies in managing the bank’s balance sheet and ensuring that the balance sheet shape and structure are robust and long-term viable.
What are the ALCO's Terms of Reference?
- A formal statement of the primary aims and objectives of the ALCO
- Its remit should cover every aspect of asset, liability and capital management of the bank’s operations
- Must include an element of oversight of credit risk
- Must be articulated clearly to all bank management
- Regular attendance by members of the ALCO must also be stressed - At the minimum, ALCO should meet every four weeks, ideally at the same time and on the same day each month
What are the main responsibilities of an ALCO?
- Approve policy and direction with respect to all aspects of balance sheet management
- Provide strategy and direction with respect to balance sheet structure and shape
- Authorise new products and processes
- Provide direction relating to the management of the bank’s liquid asset buffer
- Ensure the bank is compliant with all regulatory requirements on liquidity, funding and capital
- Meet monthly with exceptions in stressed environments
- Overseeing risks relating to liquidity, funding, capital, interest rate and FX risks - This means producing data measures; managing risk exposure through effective execution of the External Market Access Function; managing the liquid asset buffer; and reviewing limit breaches
- Provide treasury support - This includes, design of treasury policies across the business and ensuring compliance, and producing analysis and papers for monthly ALCOs
- Provide treasury services - This means proactively supporting and being involved in new product development and pricing decisions, as well as prudent management of risks
What action points are generated at the ALCO meeting?
- Management reporting - Analysing the various management reports and either signing off on them or agreeing items for action. Issues considered include:
- Lending margin
- Interest income
- Variance from last projection
- Customer business and future business
- Business planning - Exiting asset and liability books will be reviewed and future business direction is drawn up
What is the ALCO “monthly pack”?
The principle indicators are summarised in the monthly pack. It is the key bank risk report. It presents aggregate-level market risk liquidity and capital information. The preparation of this report is the responsibility of the “middle office” in banks. Ultimately it should be prepared within the Treasury department.
What is the ALCO process for identifying and categorising risk?
Generally, ALCO reporting packs employ a red-amber-green “traffic light” for each risk metric.
- If the lights are “green”, this indicates everything is in order, no limits have been breached and there is no need to dwell overmuch on that page
- An “amber” light is an advance warning of an issue that needs to be kept under watch as a potential problem
- While a “red” indication is an urgent issue that needs immediate attention
What is a GALCO?
A bank operating in a multinational environment, in which overseas entities are subsidiaries or associated legal entities rather than branches, should organise its governance via regional or legal entity ALCOs. This is then a Group ALCO - GALCO that reviews matters at the group level.
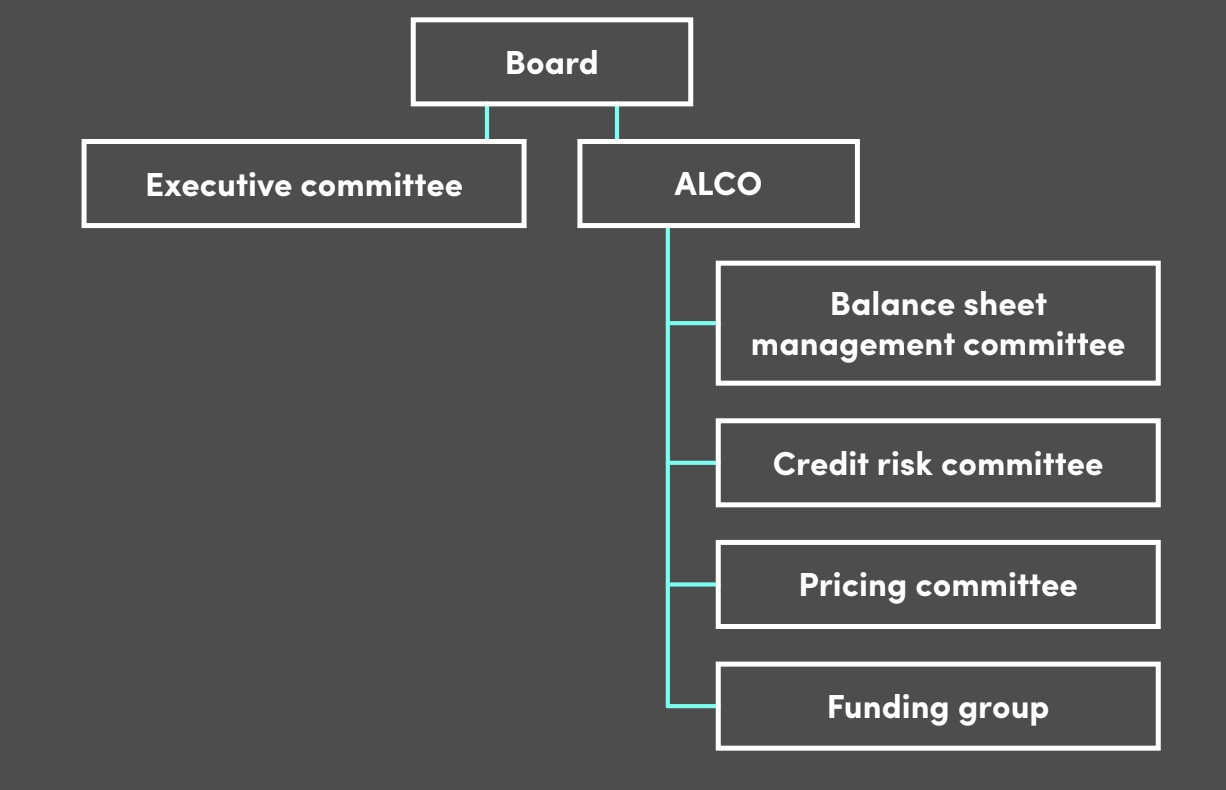
What should the ideal ALCO governance structure look like?

Moorad Choudhry
There are no available Videos from "Moorad Choudhry"

