Trade Finance as Working Capital

Aidan Applegarth
30 years: Commodity & trade finance
As explained in the previous video, once any risks are mitigated for the seller, he can raise finance against his expected sales receivable, whilst the buyer can raise finance against the security of the underlying asset. In this video we’ll see how trade working capital is enabled by deploying these solutions.
As explained in the previous video, once any risks are mitigated for the seller, he can raise finance against his expected sales receivable, whilst the buyer can raise finance against the security of the underlying asset. In this video we’ll see how trade working capital is enabled by deploying these solutions.

Trade Finance as Working Capital
4 mins 56 secs
Key learning objectives:
Learn how trade working capital is enabled
Understand why there might be no recourse
Identify the other forms of trade finance lending
Overview:
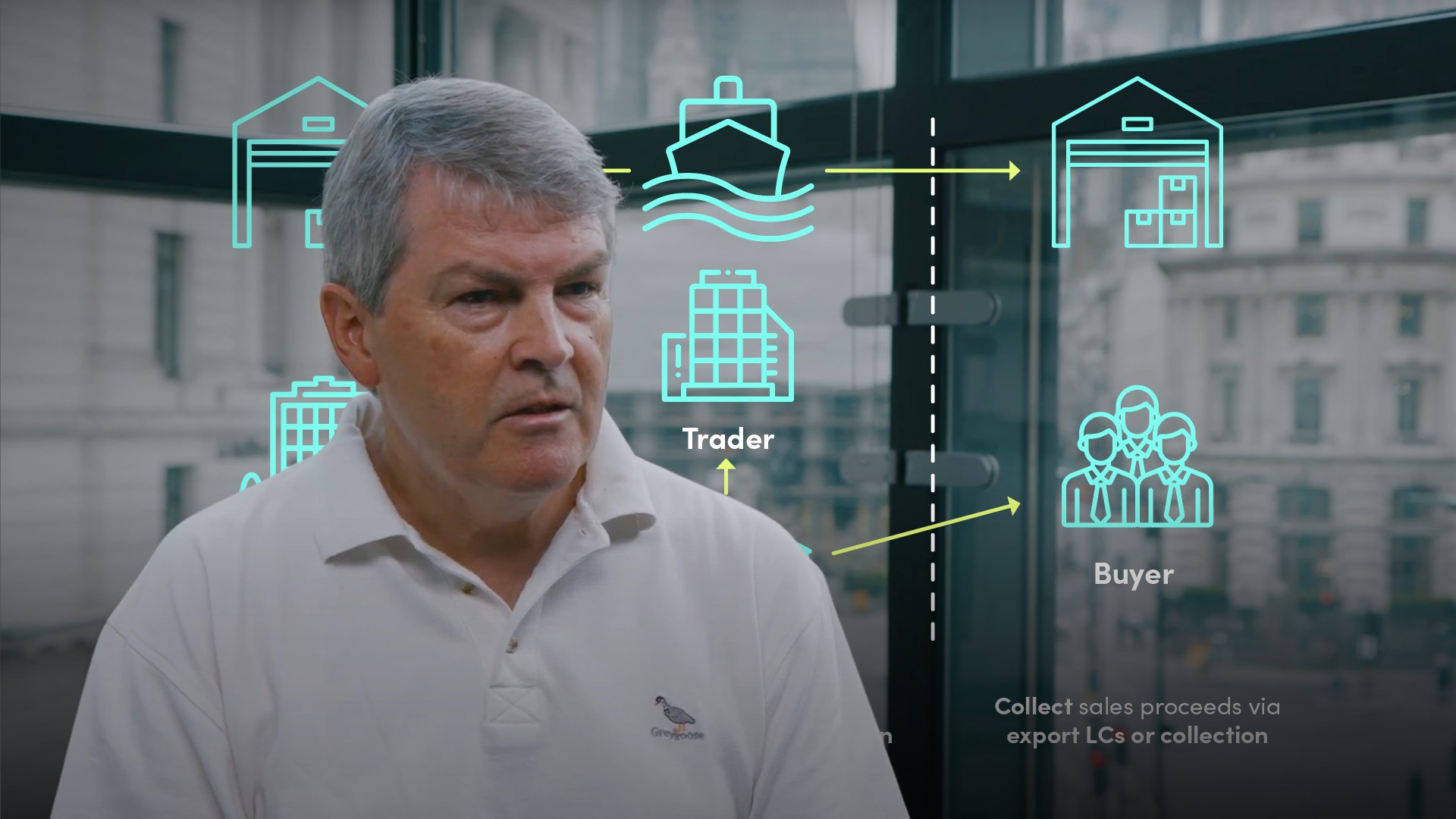
A seller can raise finance against the receivable due from his sales contracts. The more reliable the seller is in fulfilling his contracts, the more likely he can raise working capital beyond the strength of his balance sheet, thus leveraging his performance capability.
How is trade working capital enabled?
- Once the risks are mitigated for the seller, he can raise finance against his expected sales receivable
- Whilst for a buyer whose risks are also mitigated, he can raise finance against the security of the underlying asset or (if he on-sells), its receivable
What is an example of traditional trade finance?
For example, a trader who buys on the one hand and sells on the other. He probably has limited means so relies on the trade finance risk mitigants to enable the provision of working capital, essentially using the self-liquidating nature of the transaction to obtain a bridge loan between paying out for the purchase leg and receiving funds in from the sales leg.What will influence the degree of security the lender may require?
Whether any lending is ‘with’ or ‘without recourse’ to the customer. There would be a stronger security interest where there is no recourse back to the customer.Why might there be no recourse?
Some customers may not want the uncertainty of being called upon to make a good loan that they thought would be taken care of by a sales receivable, so may prefer to pay a premium to have the lender assume the underlying risks.What is the impact on the lender and seller when issuing an import LC for the purchase leg?
The lender usually acquires a lien or security interest in the goods, whilst the beneficiary (the seller) gets a bank obligation to pay which he can discount once he has complied with the terms. Discounting enables the seller to accelerate receipt of the monies due to him at small cost.What is the benefit of this form of lending?
- It affords a transparency seldom available with standard corporate lending
- Facilitates the ability to take proactive measures to protect a lender’s recourse - even if the buyer falls away, there may be opportunity to find another buyer
- Low loss default experience - where the lender has retained control to the goods or their proceeds, which rarely occurs
What are the other forms of trade finance lending?
- For a first-class seller, he may be able to obtain pre-shipment finance to enable him to buy in raw materials to meet his sales contracts
- Otherwise, the more common form of trade finance lending is post-shipment finance, which is merely accelerating the cash flow already due to the seller
- The other popular form of lending is an import loan

Aidan Applegarth
There are no available Videos from "Aidan Applegarth"

